Cataract surgery training: Report of a trainee's experience
- PMID: 37007242
- PMCID: PMC10062068
- DOI: 10.4103/ojo.ojo_128_22
Cataract surgery training: Report of a trainee's experience
Abstract
Background: To report a trainee's experience gained in the cataract extraction training program after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: An ophthalmologist was trained in phacoemulsification and intraocular lens (IOL) implantation in the ETAPE foundation, Eye Center, Cairo for a period of 4 weeks by three expert cataract surgeons. The training was tailored to the previous trainee's experience according to his residency logbook and supervised by one expert cataract surgeon. The training included didactic lectures, clinical observations, and hands-on practical experience. In addition, the trainee was provided with a logbook to record details of patients operated on and procedures observed.
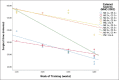
Results: The trainee performed 58 phacoemulsification surgery with IOL implantation and two extracapsular cataract extraction over the 4 weeks. Seven patients underwent intraoperative complications. Surgical time (ST) improved from 48.77 ± 9.65 min in the 1stweek to 19.34 ± 1.31 min during the last week of training (P = 0.046). Poisson regression showed that patients affected by less severe cataracts were more likely to exhibit a lower incidence of complications than patients affected by more severe cataracts. In addition, patients operated on during the 1stweek were more likely to show a higher incidence of complications than those operated on during the last week.
Conclusions: The 4-week surgical training effectively improved surgical confidence and micro incisional skills according to ST reduction and complication rate occurrence. Ophthalmologists benefit from enhancing their cataract skills in a short time following a well-structured cataract extraction course. This could undoubtedly lead to improved surgical outcomes for patients undergoing cataract extraction.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cataract surgery; ophthalmic surgery; surgical training.
Copyright: © 2023 Oman Ophthalmic Society.
Conflict of interest statement
We wish to confirm that Matteo Ripa has no conflicts of interest associated with this publication whereas Atef Sherif is employed in ETAPE foundation, Eye Center, Cairo and receive a salary for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Savastano A, Ripa M, Savastano MC, De Vico U, Caporossi T, Kilian R, et al. Comparison of novel digital microscope using integrated intraoperative OCT with Ngenuity 3D visualization system in phacoemulsification. Can J Ophthalmol. 2021 S0008-4182(21)00324-0. - PubMed
-
- Asbell PA, Dualan I, Mindel J, Brocks D, Ahmad M, Epstein S. Age-related cataract. Lancet. 2005;365:599–609. - PubMed
-
- Ferris JD, Donachie PH, Johnston RL, Barnes B, Olaitan M, Sparrow JM. Royal college of ophthalmologists' National ophthalmology database study of cataract surgery: Report 6. The impact of EyeSi virtual reality training on complications rates of cataract surgery performed by first and second year trainees. Br J Ophthalmol. 2020;104:324–9. - PubMed
-
- Saudi Commission for Health Specialties. Saudi Board ophthalmology curriculum. [Last accessed on 2022 May 01]. Available from: http://scfhs.org.sa/MESPS/TrainingProgs/TrainingProgsStatement/Documents... .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources