Retinal Detachment and Laser Retinopexy Rates During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 37007598
- PMCID: PMC9976232
- DOI: 10.1177/2474126420968407
Retinal Detachment and Laser Retinopexy Rates During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Purpose: At the start of March 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic placed an unprecedented burden on the healthcare system. Throughout much of the United States, shelter-in-place orders were imposed to reduce transmission. A consequence of this crisis, risk mitigation orders, and patient fear of exposure may have led to underutilization of emergency services. We aimed to quantify 2 emergent interventions in ophthalmology, specifically acute laser retinopexy procedures and retinal detachment repair, to determine whether these procedures decreased during the start of the pandemic.
Methods: All retinal detachment surgeries and laser retinopexy procedures were identified using Current Procedural Terminology codes. Rate data during the study period (March 1 through May 31, 2020) was compared to historical data from the year prior (March 2019 through May 2019; epoch 1) as well as the immediate 3 months prior to the study period (December 2019 through February 2020; epoch 2).
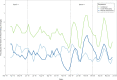
Results: Combined procedures fell by 38.5% (P = .01) and 36.0% (P = .02) when compared to epoch 1 and epoch 2, respectively. The rate of laser retinopexy procedures fell by 45.5% (P = .02) and 33.0% (P = .14) when compared to epoch 1 and epoch 2, respectively. The rate of retinal detachment repair fell by 29.4% (P = .24) and 38.0% (P = .07) when compared to epoch 1 and epoch 2, respectively.
Conclusions: Procedures fell during the study period, suggesting underutilization of emergent ophthalmology care. It is necessary for ophthalmologists to emphasize the need to seek care for concerning symptoms.
Keywords: COVID-19; coronavirus; laser retinopexy; retinal detachment.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- American Academy of Ophthalmology. Recommendations for urgent and nonurgent patient care. Published March 18, 2020. Accessed October 23, 2020. https://www.aao.org/headline/new-recommendations-urgent-nonurgent-patien...
-
- The American Society of Retina Specialists. ASRS releases guidelines to help retina practices navigate COVID-19 pandemic. Published March 18, 2020. Accessed September 6, 2020. https://www.asrs.org/clinical/clinical-updates/1962/asrs-releases-guidel...
-
- Ferrero F, Ossorio MF, Torres FA, Debaisi G. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in the paediatric emergency department attendances in Argentina. Arch Dis Child. Published online June 18, 2020. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2020-319833 - PubMed
-
- Hartnett KP, Kite-Powell A, DeVies J, et al. ; National Syndromic Surveillance Program Community of Practice. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on emergency department visits—United States, January 1, 2019-May 30, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(23):699–704. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6923e1 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources