Expressions of the Protein Phosphatases PP1 and PP4 during the Embryonic Diapause Process of the Silkworm Bombyx mori
- PMID: 37007811
- PMCID: PMC10061206
- DOI: 10.6620/ZS.2022.61-61
Expressions of the Protein Phosphatases PP1 and PP4 during the Embryonic Diapause Process of the Silkworm Bombyx mori
Abstract
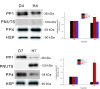
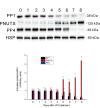
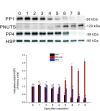
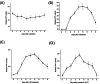
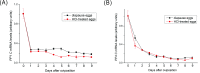
Reversible protein phosphorylation is accomplished by the opposing activities of kinases and phosphatases. We previously demonstrated the regulation of serine/threonine protein phosphatase (PP) type 2A (PP2A) and 2B (PP2B or calcineurin) during the embryonic diapause process of Bombyx mori. In the present study, we further examine the expressions of other PPs (PP1 and PP4) during embryonic stages. An immunoblot analysis showed that Bombyx eggs contained a 38-kDa PP1 catalytic subunit (PP1-C), a 38-kDa PP4 catalytic subunit (PP4-C), and a 120-kDa PP1 nuclear targeting subunit (PNUTS), each of which underwent differential changes between diapause and developing eggs during the embryonic process. In non-diapause eggs, eggs whose diapause initiation was prevented by HCl, and eggs in which diapause had been terminated by chilling diapausing eggs at 5°C for 70 days and then were transferred to 25°C, protein levels of PP1-C and PP4-C remained relatively high during the early embryonic stages and then decreased during middle (for PP1-C) or later (for PP4-C) embryonic stages. However, protein levels of PP1-C and PP4-C in diapause eggs remained at high levels during the first 8 days after oviposition. PNUTS protein levels showed inverse temporal changes, with increased levels being detected during the later embryonic stages of developing eggs. The direct determination of PP1 enzymatic activity showed higher activity in developing eggs than in diapause eggs. Examination of temporal changes in mRNA expression levels of PP1-C and PP4-C showed no difference between HCl-treated and diapause eggs. These results indicated that differential protein levels of PP1-C/PNUTS and PP4-C, and increased enzymatic activity of PP1 were likely related to the embryonic development of B. mori.
Keywords: Bombyx mori; Diapause; Gene expression; PNUTS; PP1; PP4; Phosphatase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of protein phosphatase 2A during embryonic diapause process in the silkworm, Bombyx mori.J Insect Physiol. 2017 Nov;103:117-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Sep 8. J Insect Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28893508
-
Expression of protein tyrosine phosphatases and Bombyx embryonic development.J Insect Physiol. 2021 Apr;130:104198. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2021.104198. Epub 2021 Feb 4. J Insect Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33549567
-
Expression of calcineurin in relation to the embryonic diapause process in the silkworm, Bombyx mori.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2019 Feb;228:35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.10.013. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30367963
-
Expression of protein kinase C in relation to the embryonic diapause process in the silkworm, Bombyx mori.J Insect Physiol. 2020 Feb-Mar;121:104010. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2019.104010. Epub 2020 Jan 7. J Insect Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31917243
-
Ecdysteroids during early embryonic development in silkworm Bombyx mori: metabolism and functions.Zoolog Sci. 2004 May;21(5):503-16. doi: 10.2108/zsj.21.503. Zoolog Sci. 2004. PMID: 15170054 Review.
References
-
- Allen PB, Kwon YG, Nairn AC, Greengard P. 1998. Isolation and characterization of PNUTS, a putative protein phosphatase 1 nuclear targeting subunit. J Biol Chem 273:4089–4095. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.7.4089. - PubMed
-
- Axton JM, Dombrádi V, Cohen PT, Glover DM. 1990. One of the protein phosphatase 1 isoenzymes in Drosophila is essential for mitosis. Cell 63:33–46. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(90)90286-n. - PubMed
-
- Bhaskar PT, Hay N. 2007. The two TORCs and Akt. Dev Cell 12:487–502. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2007.03.020. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
