Inter- and Intra-rater Reliability of Modified House-Brackmann and Sunnybrook Facial Nerve Grading Systems in Post Parotidectomy Patients
- PMID: 37007896
- PMCID: PMC10050663
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-022-03140-y
Inter- and Intra-rater Reliability of Modified House-Brackmann and Sunnybrook Facial Nerve Grading Systems in Post Parotidectomy Patients
Abstract
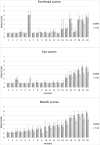
To compare inter-rater, intra-rater and inter-system reliability of modified House-Brackmann and Sunnybrook grading systems. The study was conducted in a tertiary care hospital with a single cohort of 20 patients and 3 raters. The patients, eligible to be included for the study, were those over 18 years of age planned for nerve sparing parotidectomy. In the postoperative period, patients were video recorded performing specific movements according to the requirements of modified House-Brackmann and Sunnybrook systems. These recordings were used for the grading once recruitment was completed. The inter-rater, intra-rater and inter-system reliability of modified House-Brackmann and Sunnybrook systems were assessed using the intraclass coefficient. The intra-rater reliability was good-to-excellent for both groups with Intra-Class coefficient (ICC) ranging from 0.902 to 0.958 in modified House-Brackmann and in 0.802 to 0.957 Sunnybrook system. The inter-rater reliability was good-to-excellent with ICC ranging from 0.806 to 0.906 in modified House-Brackmann and 0.766 to 0.860 in Sunnybrook system. The inter-system reliability was good-to-excellent with ICC ranging from 0.892 to 0.937. There was no significant difference in the reliability of modified House-Brackmann and Sunnybrook systems. Thus, an interval scale accomplishes the task of grading facial nerve palsy in a reliable way, and the choice of the specific instrument will be based on other factors like expertise involved, ease of administration and generalisability to the incumbent clinical scenario.
Keywords: Facial nerve; Grading; House-Brackmann; Parotidectomy; Sunnybrook.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Coulson SE, Croxson GR, Adams RD, Odwyer NJ. Reliability of the “Sydney”, “Sunnybrook”, and “House Brackmann” facial grading systems to assess voluntary movement and synkinesis after facial nerve paralysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;132:543–549. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2005.01.027. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources