Erdafitinib-Induced Secondary Maculopathy
- PMID: 37007917
- PMCID: PMC9976033
- DOI: 10.1177/24741264221092908
Erdafitinib-Induced Secondary Maculopathy
Abstract
Purpose: This work presents a case of secondary maculopathy associated with the use of erdafitinib (Balversa) for the management of bladder urothelial carcinoma with bony metastasis.
Methods: A case report is presented.
Results: A 58-year-old Hispanic man presented with blurry vision 3 weeks after starting erdafitinib for the management of bony metastases associated with urothelial carcinoma. A comprehensive evaluation identified multiple areas of subretinal fluid induced by erdafitinib. Throughout treatment, the ocular condition progressed, causing worsening of vision; this led to discontinuation of the drug. Discontinuation was associated with visual and anatomic function improvement.
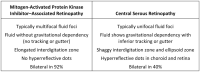
Conclusions: Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) plays a major role in maintaining mature and premature retinal pigment epithelium cells. Drugs that inhibit the FGFR pathway block the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, leading to synthesis of antiapoptotic proteins. Erdafitinib is associated with ocular toxicity and leads to multifocal pigment epithelial detachments associated with secondary subretinal fluid.
Keywords: FGFR; MAPK; RPE detachment; central serous chorioretinopathy; erdafitinib; mitogen-activated protein kinase retinopathy; targeted therapy.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Jansen. (n.d.). Balversa. Prescribing information. Accessed October/November 2021. https://www.janssenlabels.com/package-insert/product-monograph/prescribi...
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

