Recent Advances in Nano-Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Diabetic Wound Healing
- PMID: 37007988
- PMCID: PMC10065433
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S395438
Recent Advances in Nano-Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Diabetic Wound Healing
Abstract
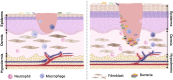
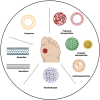
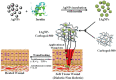
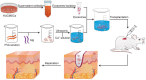
Diabetes mellitus (DM) induced wound healing impairment remains a serious health problem and burden on the clinical obligation for high amputation rates. Based on the features of wound microenvironment, biomaterials loading specific drugs can benefit diabetic wound treatment. Drug delivery systems (DDSs) can carry diverse functional substances to the wound site. Nano-drug delivery systems (NDDSs), benefiting from their features related to nano size, overcome limitations of conventional DDSs application and are considered as a developing process in the wound treatment field. Recently, a number of finely designed nanocarriers efficiently loading various substances (bioactive and non-bioactive factors) have emerged to circumvent constraints faced by traditional DDSs. This review describes various recent advances of nano-drug delivery systems involved in mitigating diabetes mellitus-based non-healing wounds.
Keywords: diabetic wound healing; drug delivery system; nanoparticles; nanotechnology.
© 2023 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

