Recombinant irisin prevents cell death and mineralization defects induced by random positioning machine exposure in primary cultures of human osteoblasts: A promising strategy for the osteoporosis treatment
- PMID: 37008023
- PMCID: PMC10052411
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1107933
Recombinant irisin prevents cell death and mineralization defects induced by random positioning machine exposure in primary cultures of human osteoblasts: A promising strategy for the osteoporosis treatment
Abstract
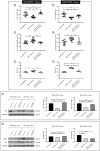
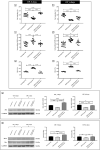
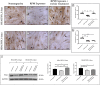
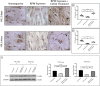
Spaceflight exposure, like prolonged skeletal unloading, is known to result in significant bone loss, but the molecular mechanisms responsible are still partly unknown. This impairment, characterizing both conditions, suggests the possibility of identifying common signalling pathways and developing innovative treatment strategies to counteract the bone loss typical of astronauts and osteoporotic patients. In this context, primary cell cultures of human osteoblasts derived from healthy subjects and osteoporotic patients were exposed to random positioning machine (RPM) to reproduce the absence of gravity and to exacerbate the pathological condition, respectively. The duration of exposure to RPM was 3 or 6 days, with the aim of determining whether a single administration of recombinant irisin (r-irisin) could prevent cell death and mineralizing capacity loss. In detail, cellular responses were assessed both in terms of death/survival, by MTS assay, analysis of oxidative stress and caspase activity, as well as the expression of survival and cell death proteins, and in terms of mineralizing capacity, by investigating the pentraxin 3 (PTX3) expression. Our results suggest that the effects of a single dose of r-irisin are maintained for a limited time, as demonstrated by complete protection after 3 days of RPM exposure and only partial protection when RPM exposure was for a longer time. Therefore, the use of r-irisin could be a valid strategy to counteract the bone mass loss induced by weightlessness and osteoporosis. Further studies are needed to determine an optimal treatment strategy based on the use of r-irisin that is fully protective even over very long periods of exposure and/or to identify further approaches to be used in a complementary manner.
Keywords: apoptosis; bone loss; cell viability; mineralization; random positioning machine; recombinant irisin; simulated microgravity.
Copyright © 2023 Cariati, Bonanni, Rinaldi, Marini, Iundusi, Gasbarra, Tancredi and Tarantino.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exposure to Random Positioning Machine Alters the Mineralization Process and PTX3 Expression in the SAOS-2 Cell Line.Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 19;12(5):610. doi: 10.3390/life12050610. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629278 Free PMC article.
-
Trolox and recombinant Irisin as a potential strategy to prevent neuronal damage induced by random positioning machine exposure in differentiated HT22 cells.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 21;19(3):e0300888. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300888. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38512830 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant Irisin Prevents the Reduction of Osteoblast Differentiation Induced by Stimulated Microgravity through Increasing β-Catenin Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 13;21(4):1259. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041259. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32070052 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of irisin on bone in osteoporosis: a systematic review of rodent studies.Osteoporos Int. 2025 Apr 7. doi: 10.1007/s00198-025-07470-9. Online ahead of print. Osteoporos Int. 2025. PMID: 40192854 Review.
-
Irisin and Secondary Osteoporosis in Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 8;23(2):690. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020690. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054874 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stromal Lineage Precursors from Rodent Femur and Tibia Bone Marrows after Hindlimb Unloading: Functional Ex Vivo Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 11;24(10):8594. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108594. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239936 Free PMC article.
-
Numerical study of interstitial fluid flow behavior in osteons under dynamic loading.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Feb 24;26(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08425-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 39994737 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress on the Ground and in the Microgravity Environment: Pathophysiological Effects and Treatment.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Feb 18;14(2):231. doi: 10.3390/antiox14020231. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting ERRs to counteract age-related muscle atrophy associated with physical inactivity: a pilot study.Front Physiol. 2025 Jul 7;16:1616693. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1616693. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40692696 Free PMC article.
-
A pilot study: effect of irisin on trabecular bone in a streptozotocin-induced animal model of type 1 diabetic osteopathy utilizing a micro-CT.PeerJ. 2023 Oct 17;11:e16278. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16278. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37868046 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

