Generating Flavor Molecules Using Scientific Machine Learning
- PMID: 37008127
- PMCID: PMC10061502
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c07176
Generating Flavor Molecules Using Scientific Machine Learning
Abstract
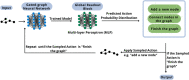
Flavor is an essential component in the development of numerous products in the market. The increasing consumption of processed and fast food and healthy packaged food has upraised the investment in new flavoring agents and consequently in molecules with flavoring properties. In this context, this work brings up a scientific machine learning (SciML) approach to address this product engineering need. SciML in computational chemistry has opened paths in the compound's property prediction without requiring synthesis. This work proposes a novel framework of deep generative models within this context to design new flavor molecules. Through the analysis and study of the molecules obtained from the generative model training, it was possible to conclude that even though the generative model designs the molecules through random sampling of actions, it can find molecules that are already used in the food industry, not necessarily as a flavoring agent, or in other industrial sectors. Hence, this corroborates the potential of the proposed methodology for the prospecting of molecules to be applied in the flavor industry.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


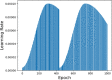


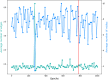
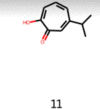



References
-
- Berenstein N.Flavor Added: The Sciences of Flavor and the Industrialization of Taste in America. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses, 2018, p 556.
-
- Ulloa A. M. The aesthetic life of artificial flavors. Senses Soc. 2018, 13, 60–74. 10.1080/17458927.2017.1420026. - DOI
-
- Monteiro A.; Costa P.; Loureiro J. M.; Rodrigues A. E. Flavor Engineering-A Methodology to Predict Sensory Qualities of Flavored Products. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 8115–8123. 10.1021/acs.iecr.8b00527. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

