Antibiotic Adjuvants: A Versatile Approach to Combat Antibiotic Resistance
- PMID: 37008128
- PMCID: PMC10061514
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00312
Antibiotic Adjuvants: A Versatile Approach to Combat Antibiotic Resistance
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Antibiotic Adjuvants: A Versatile Approach to Combat Antibiotic Resistance.ACS Omega. 2023 May 24;8(22):20148-20150. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03063. eCollection 2023 Jun 6. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37305280 Free PMC article.
-
Correction to "Antibiotic Adjuvants: A Versatile Approach to Combat Antibiotic Resistance".ACS Omega. 2024 Jun 18;9(26):29070-29071. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05153. eCollection 2024 Jul 2. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38973872 Free PMC article.
Abstract
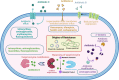
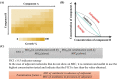
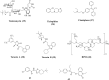
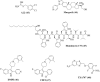
The problem of antibiotic resistance is on the rise, with multidrug-resistant strains emerging even to the last resort antibiotics. The drug discovery process is often stalled by stringent cut-offs required for effective drug design. In such a scenario, it is prudent to delve into the varying mechanisms of resistance to existing antibiotics and target them to improve antibiotic efficacy. Nonantibiotic compounds called antibiotic adjuvants which target bacterial resistance can be used in combination with obsolete drugs for an improved therapeutic regime. The field of "antibiotic adjuvants" has gained significant traction in recent years where mechanisms other than β-lactamase inhibition have been explored. This review discusses the multitude of acquired and inherent resistance mechanisms employed by bacteria to resist antibiotic action. The major focus of this review is how to target these resistance mechanisms by the use of antibiotic adjuvants. Different types of direct acting and indirect resistance breakers are discussed including enzyme inhibitors, efflux pump inhibitors, inhibitors of teichoic acid synthesis, and other cellular processes. The multifaceted class of membrane-targeting compounds with poly pharmacological effects and the potential of host immune-modulating compounds have also been reviewed. We conclude with providing insights about the existing challenges preventing clinical translation of different classes of adjuvants, especially membrane-perturbing compounds, and a framework about the possible directions which can be pursued to fill this gap. Antibiotic-adjuvant combinatorial therapy indeed has immense potential to be used as an upcoming orthogonal strategy to conventional antibiotic discovery.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures







References
-
- O’Neill J.Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; Wellcome Trust; HM Government, 2016.
-
- Top Ten causes of death. 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed January 1, 2023).
-
- Global AntimicrobialResistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report 2022. 2022. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240062702 (accessed January 12, 2023).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

