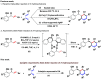
Catalytic Asymmetric Diels-Alder Reaction of 2'-Hydroxychalcone as a Dienophile with a VANOL-Borate Ester Complex
- PMID: 37008159
- PMCID: PMC10061623
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00782
Catalytic Asymmetric Diels-Alder Reaction of 2'-Hydroxychalcone as a Dienophile with a VANOL-Borate Ester Complex
Abstract
Numerous flavonoid Diels-Alder-type natural products have been isolated and received great attention from the synthetic community. Herein, we reported a catalytic strategy for an asymmetric Diels-Alder reaction of 2'-hydroxychalcone with a range of diene substrates using a chiral ligand-boron Lewis acid complex. This method enables the convenient synthesis of a wide range of cyclohexene skeletons in excellent yields with moderate to good enantioselectivities, which is critical to prepare natural product congeners for further biological studies.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nomura T.; Hano Y. Isoprenoid-substituted phenolic compounds of moraceous plants. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1994, 11, 205–218. 10.1039/np9941100205. - DOI - PubMed
- Nomura T. The chemistry and biosynthesis of isoprenylated flavonoids from moraceous plants. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 1115–1118. 10.1351/pac199971061115. - DOI
- Nomura T.; Hano Y.; Fukai T. Chemistry and biosynthesis of isoprenylated flavonoids from Japanese mulberry tree. Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B 2009, 85, 391–408. 10.2183/pjab.85.391. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nomura T.; Fukai T.; Hano Y. Bioactive Natural Products. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2003, 28, 199–256.
- Tortora C.; Pisano L.; Vergine V.; Ghirga F.; Iazzetti A.; Calcaterra A.; Markovic V.; Botta B.; Quaglio D. Synthesis, Biosynthesis, and Biological Activity of Diels–Alder Adducts from Morus Genus: An Update. Molecules 2022, 27, 7580.10.3390/molecules27217580. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Luo S.-Y.; Zhu J.-Y.; Zou M.-F.; Yin S.; Tang G.-H. Mulberry Diels-Alder-type adducts: isolation, structure, bioactivity, and synthesis. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect 2022, 12, 31.10.1007/s13659-022-00355-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kirana C.; Jones G. P.; Record I. R.; McIntosh G. H. Anticancer properties of panduratin A isolated from Boesenbergia pandurata (Zingiberaceae). J. Nat. Med. 2007, 61, 131–137. 10.1007/s11418-006-0100-0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources