Traditional Chinese Manual Therapy (Tuina) reshape the function of default mode network in patients with lumbar disc herniation
- PMID: 37008205
- PMCID: PMC10050335
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1125677
Traditional Chinese Manual Therapy (Tuina) reshape the function of default mode network in patients with lumbar disc herniation
Abstract
Purpose: Investigating the changes of regional homogeneity (ReHo) values and both static and dynamic functional connectivity (FC) before and after Traditional Chinese Manual Therapy (Tuina) in patients with lumbar disk herniation (LDH) through resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (RS-fMRI). Based on this, we observe the effect of Tuina on the above abnormal changes.
Methods: Patients with LDH (n = 27) and healthy controls (HCs) (n = 28) were recruited. The functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scanning was performed two times in LDH patients, before Tuina (time point 1, LDH-pre) and after the sixth Tuina (time point 2, LDH-pos). And for one time in HCs which received no intervention. The ReHo values were compared between LDH-pre and HCs. The significant clusters detected by ReHo analysis were selected as seeds to calculate static functional connectivity (sFC). We also applied the sliding-window to perform dynamic functional connectivity (dFC). To evaluate the Tuina effect, the mean ReHo and FC values (both static and dynamic) were extracted from significant clusters and compared between LDH and HCs.
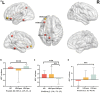
Results: In comparison to HCs, LDH patients displayed decreased ReHo in the left orbital part middle frontal gyrus (LO-MFG). For sFC analysis, no significant difference was found. However, we found decreased dFC variance between LO-MFG and the left Fusiform, and increased dFC variance in the left orbital inferior frontal gyrus and left precuneus. Both ReHo and dFC values revealed after Tuina, the brain activities in LDH patients were similar to HCs.
Conclusion: The present study characterized the altered patterns of regional homogeneity in spontaneous brain activity and those of functional connectivity in patients with LDH. Tuina can reshape the function of the default mode network (DMN) in LDH patients, which may contribute to the analgesic effect of Tuina in LDH patients.
Keywords: Tuina; functional connectivity; lumbar disc herniation; regional homogeneity; resting-state fMRI.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Wen, Chen, Jin, Liu, Wang, Kong, Ling, Huang, Chai, Zhao, Li, Xu, Jiang and Du.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Al Qaraghli M. I., De Jesus O. (2022). Lumbar Disc Herniation. Statpearls. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing. - PubMed
-
- Beelen C., Blockmans L., Wouters J., Ghesquière P., Vandermosten M. (2022). Brain-behavior dynamics between the left fusiform and reading. Brain Struct. Funct. 227 587–597. - PubMed
-
- de Zoete A., Rubinstein S. M., De Boer M. R., Ostelo R., Underwood M., Hayden J. A., et al. (2021). The effect of spinal manipulative therapy on pain relief and function in patients with chronic low back pain: an individual participant data meta-analysis. Physiotherapy 112 121–134. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

