Identification of anthropometric surrogate measurements and their cut-off points for the detection of low birth weight and premature newborn babies using ROC Analysis
- PMID: 37008417
- PMCID: PMC10052390
- DOI: 10.1017/jns.2023.20
Identification of anthropometric surrogate measurements and their cut-off points for the detection of low birth weight and premature newborn babies using ROC Analysis
Abstract
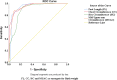
Despite the fact that health facilities in Ethiopia are being built closer to communities in all regions, the proportion of home deliveries remains high, and there are no studies being conducted to identify low birth weight (LBW) and premature newborn babies using simple, best, alternative, and appropriate anthropometric measurement in the study area. The objective of the present study was to find the simple, best, and alternative anthropometric measurement and identified its cut-off points for detecting LBW and premature newborn babies. A health facility-based cross-sectional study was conducted in the Dire Dawa city administration, Eastern Ethiopia. The study included 385 women who gave birth in health facility. To evaluate the overall accuracy of the anthropometric measurements, a non-parametric receiver operating characteristic curve was used. Chest circumference (AUC = 0⋅95) with 29⋅4 cm and mean upper arm circumference (AUC = 0⋅93) with 7⋅9 cm proved to be the best anthropometric diagnostic measure for LBW and gestational age, respectively. Also, both anthropometric measuring tools are achieved the highest correlation (r = 0⋅62) for LBW and gestational age. Foot length had a higher sensitivity (94⋅8 %) in detecting LBW than other measurements, with a higher negative predictive value (NPV) (98⋅4 %) and a higher positive predictive value (PPV) (54⋅8 %). Chest circumference and mid-upper arm circumference were found to be better surrogate measurements for identifying LBW and premature babies in need of special care. More research is needed to identify better diagnostic interventions in situations like the study area, which has limited resources and a high proportion of home deliveries.
Keywords: AUC, area under curve; Anthropometric measurement; BW, birth weight; CC, chest circumference; CI, confidence interval; DHS, Demographic and Health Survey; DOR, diagnostic odds ratio; EMDHS, Ethiopia Mini Demographic and Health Survey; FL, foot length; GA, gestational age; HC, head circumference; LBW; LBW, low birth weight; MUAC, mid-upper arm circumference; NICU, neonatal intensive care unit; NPV, negative predictive value; Non-parametric; PPV, positive predictive value; ROC analysis; ROC, receiver operating characteristics; WHO, World Health Organization.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Figures
References
-
- Estimation UNI-aGfCM (2020) Levels & Trends in Child Mortality: Report 2020, Estimates Developed by the UN Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation.
-
- Estimation UNI-aGfCM (2020) Levels and Trends in Child mortality: Report 2020. Fund UNCs New York.
-
- Dubois L & Girard M (2006) Determinants of birthweight inequalities: population-based study. Pediatr Int 48, 470–478. - PubMed
-
- Goldenberg RL & Culhane JF (2007) Low birth weight in the United States. Am J Clin Nutr 85, 584S–590S. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources