Role of soy lecithin combined with soy isoflavone on cerebral blood flow in rats of cognitive impairment and the primary screening of its optimum combination
- PMID: 37009142
- PMCID: PMC10042711
- DOI: 10.4162/nrp.2023.17.2.371
Role of soy lecithin combined with soy isoflavone on cerebral blood flow in rats of cognitive impairment and the primary screening of its optimum combination
Abstract
Background/objectives: Soy isoflavone (SIF) and soy lecithin (SL) have beneficial effects on many chronic diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases. Regretfully, there is little evidence to show the combined effects of these soy extractives on the impairment of cognition and abnormal cerebral blood flow (CBF). This study examined the optimal combination dose of SIF + SL to provide evidence for improving CBF and protecting cerebrovascular endothelial cells.
Materials/methods: In vivo study, SIF50 + SL40, SIF50 + SL80 and SIF50 + SL160 groups were obtained. Morris water maze, laser speckle contrast imaging (LSCI), and hematoxylin-eosin staining were used to detect learning and memory impairment, CBF, and damage to the cerebrovascular tissue in rat. The 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and the oxidized glutathione (GSSG) were detected. The anti-oxidative damage index of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH) in the serum of an animal model was also tested. In vitro study, an immortalized mouse brain endothelial cell line (bEND.3 cells) was used to confirm the cerebrovascular endothelial cell protection of SIF + SL. In this study, 50 μM of Gen were used, while the 25, 50, or 100 μM of SL for different incubation times were selected first. The intracellular levels of 8-OHdG, SOD, GSH, and GSSG were also detected in the cells.
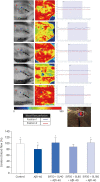
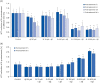
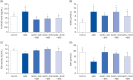
Results: In vivo study, SIF + SL could increase the target crossing times significantly and shorten the total swimming distance of rats. The CBF in the rats of the SIF50 + SL40 group and SIF50 + SL160 group was enhanced. Pathological changes, such as attenuation of the endothelium in cerebral vessels were much less in the SIF50 + SL40 group and SIF50 + SL160 group. The 8-OHdG was reduced in the SIF50 + SL40 group. The GSSG showed a significant decrease in all SIF + SL pretreatment groups, but the GSH showed an opposite result. SOD was upregulated by SIF + SL pretreatment. Different combinations of Genistein (Gen)+SL, the secondary proof of health benefits found in vivo study, showed they have effective anti-oxidation and less side reaction on protecting cerebrovascular endothelial cell. SIF50 + SL40 in rats experiment and Gen50 + SL25 in cell test were the optimum joint doses on alleviating cognitive impairment and regulating CBF through protecting cerebrovascular tissue by its antioxidant activity.
Conclusions: SIF+SL could significantly prevent cognitive defect induced by β-Amyloid through regulating CBF. This kind of effect might be attributed to its antioxidant activity on protecting cerebral vessels.
Keywords: Cerebral blood flow; beta-amyloid peptide; cognitive impairment; isoflavone; lecithin.
©2023 The Korean Nutrition Society and the Korean Society of Community Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interests.
Figures




References
-
- Wu HZ, Ong KL, Seeher K, Armstrong NJ, Thalamuthu A, Brodaty H, Sachdev P, Mather K. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;49:755–766. - PubMed
-
- Rius-Pérez S, Tormos AM, Pérez S, Taléns-Visconti R. Vascular pathology: cause or effect in Alzheimer disease? Neurologia (Engl Ed) 2018;33:112–120. - PubMed
-
- Xi YD, Yu HL, Ding J, Ma WW, Yuan LH, Feng JF, Xiao YX, Xiao R. Flavonoids protect cerebrovascular endothelial cells through Nrf2 and PI3K from β-amyloid peptide-induced oxidative damage. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2012;9:32–41. - PubMed
-
- Soybean IS. Soybean and processed soy foods ingredients, and their role in cardiometabolic risk prevention. Recent Pat Food Nutr Agric. 2015;7:75–82. - PubMed

