COVID-19 and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Literature Review From Pathogenesis to Diagnosis
- PMID: 37009373
- PMCID: PMC10065369
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.35658
COVID-19 and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Literature Review From Pathogenesis to Diagnosis
Abstract
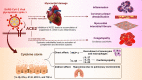
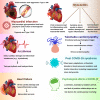
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) took the world by storm after the first case of COVID-19 emerged in China on December 8, 2019. The disease is generally considered as an infection of the respiratory system, but serious life-threatening myocardial injuries have been reported with this infection. Coronavirus can damage cardiac myocytes by entering the cell through angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) receptor binding. Myocardial infarction, myocarditis, heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy are cardiac clinical manifestations commonly seen among patients affected by COVID-19. These cardiac pathologies are seen both during ongoing infection and post-infection. Elevated levels of myoglobin, troponin, creatine kinase-MB, plasma interleukin-6, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and N-terminal pro-b-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) have been found in COVID-19-associated myocardial injuries. The diagnostic modalities used in myocardial injuries due to COVID-19 include electrocardiography (ECG), cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR), endomyocardial biopsy, echocardiography (Echo), and computerized tomography (CT-Scan). This literature review will discuss, in detail, the pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis of myocardial injuries due to COVID-19.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; cardiovascular insult; covid-19; dysrhythmia; echocardiography; myocardial injuries; myocarditis; sars-cov-2; troponin.
Copyright © 2023, Naeem et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Wu Z, McGoogan JM. JAMA. 2020;323:1239–1242. - PubMed
-
- Coronavirus Cases: Statistics and Charts - Worldometer. [ Jan; 2023 ]. 2023. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/coronavirus-cases/ https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/coronavirus-cases/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
