SOCRAT: a Dynamic Web Toolbox for Interactive Data Processing, Analysis and Visualization
- PMID: 37009525
- PMCID: PMC10062429
- DOI: 10.3390/info13110547
SOCRAT: a Dynamic Web Toolbox for Interactive Data Processing, Analysis and Visualization
Abstract
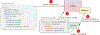
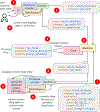
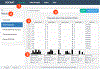
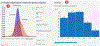
Many systems for exploratory and visual data analytics require platform-dependent software installation, coding skills, and analytical expertise. The rapid advances in data-acquisition, web-based information, and communication and computation technologies promoted the explosive growth of online services and tools implementing novel solutions for interactive data exploration and visualization. However, web-based solutions for visual analytics remain scattered and relatively problem-specific. This leads to per-case re-implementations of common components, system architectures, and user interfaces, rather than focusing on innovation and building sophisticated applications for visual analytics. In this paper, we present the Statistics Online Computational Resource Analytical Toolbox (SOCRAT), a dynamic, flexible, and extensible web-based visual analytics framework. The SOCRAT platform is designed and implemented using multi-level modularity and declarative specifications. This enables easy integration of a number of components for data management, analysis, and visualization. SOCRAT benefits from the diverse landscape of existing in-browser solutions by combining them with flexible template modules into a unique, powerful, and feature-rich visual analytics toolbox. The platform integrates a number of independently developed tools for data import, display, storage, interactive visualization, statistical analysis, and machine learning. Various use cases demonstrate the unique features of SOCRAT for visual and statistical analysis of heterogeneous types of data.
Keywords: exploratory analysis; statistical visualization; visual analytics; web toolkits.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- McAfee A; Brynjolfsson E Big data: the management revolution. Harv. Bus. Rev 2012, 90, 60–6, 68, 128. - PubMed
-
- Dinov ID Data Science and Predictive Analytics: Biomedical and Health Applications using R; Springer, 2018. 10.1007/978-3-319-72347-1. - DOI
-
- Dinov ID; Velev MV Data science: Time complexity, inferential uncertainty, and spacekime analytics; De Gruyter STEM, De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2021. 10.1515/9783110697827. - DOI
-
- Keim D; Andrienko G; Fekete JD; Görg C; Kohlhammer J; Melançon G Visual Analytics: Definition, Process, and Challenges. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; pp. 154–175. 10.1007/978-3-540-70956-5_7. - DOI
-
- Liu S; Cui W; Wu Y; Liu M A survey on information visualization: recent advances and challenges. Vis. Comput 2014, 30, 1373–1393. 10.1007/s00371-013-0892-3. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
