Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors and the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 37010128
- PMCID: PMC10267615
- DOI: 10.1093/ajh/hpad031
Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors and the COVID-19 Pandemic
Keywords: 2; ACE2; COVID-19 pandemic; SARS-COV; blood pressure; cardiovascular disease; hypertension; renin-angiotensin system inhibitors.
Figures
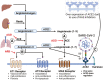
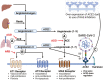
Comment on
-
Discontinuation of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors During the Early Stage of the COVID-19 Pandemic.Am J Hypertens. 2023 Jun 15;36(7):404-410. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpad027. Am J Hypertens. 2023. PMID: 36960855 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Hypothesis for renin-angiotensin inhibitor mitigation of COVID-19.Med Hypotheses. 2021 Jul;152:110609. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2021.110609. Epub 2021 May 12. Med Hypotheses. 2021. PMID: 34048987 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and renin-angiotensin system inhibition: role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) - Is there any scientific evidence for controversy?J Intern Med. 2020 Oct;288(4):410-421. doi: 10.1111/joim.13101. Epub 2020 Jun 8. J Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32459372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and the renin-angiotensin system: A closer look at angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2).Ann Clin Biochem. 2020 Sep;57(5):339-350. doi: 10.1177/0004563220928361. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Ann Clin Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32369402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).J Pathol. 2020 Jul;251(3):228-248. doi: 10.1002/path.5471. Epub 2020 Jun 10. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32418199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanistic overview of SARS-CoV-2 using angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 to enter the cell for replication: possible treatment options related to the renin-angiotensin system.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2020 Sep 1;6(5):317-325. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa053. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32464637 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

