Factors associated with caregiver burden among family caregivers of children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review
- PMID: 37012010
- PMCID: PMC10083783
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065215
Factors associated with caregiver burden among family caregivers of children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review
Abstract
Objectives: To identify caregiver and children factors associated with caregiver burden on primary caregivers of children with cerebral palsy (CP).
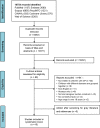
Design: Systematic review DATA SOURCES: Seven electronic databases, including PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, PsycINFO, Web of Science, CINAHL and Embase, were systematically searched up to 1 February 2023.
Eligibility criteria: Original observational studies reporting caregiver burden and related factors among caregivers of children with CP.
Data abstraction and synthesis: Two reviewers independently screened results and assessed the quality of studies. Title, abstract, full-text screening and data abstraction were done independently by two reviewers. Risk of bias was assessed using the JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Analytical Cross-Sectional Studies. The quality of evidence for factors was rated using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach.
Results: 16 articles were included in the review. All studies were cross-sectional and examined caregiver-reported burden measures. The Zarit Burden Interview was the most commonly used questionnaire. Depression of caregiver and severity of illness in children with CP were moderate quality of evidence for factors contributing to caregiver burden.
Conclusions: Higher caregiver burden is associated with more depressive feelings and worse life quality of the caregiver, and with more severe physical disability of the children. Future studies should focus on high-quality longitudinal research and appropriate assistance to reduce caregiver burden and improve the quality of caregiving for children with CP.
Prospero registration number: CRD42021268284.
Keywords: developmental neurology & neurodisability; primary care; rehabilitation medicine.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous