Study protocol of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-arm parallel-group, multi-centre phase 3 pivotal trial to investigate the efficacy and safety of recombinant human alkaline phosphatase for treatment of patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- PMID: 37012016
- PMCID: PMC10083765
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065613
Study protocol of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-arm parallel-group, multi-centre phase 3 pivotal trial to investigate the efficacy and safety of recombinant human alkaline phosphatase for treatment of patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
Abstract
Introduction: Sepsis, the leading cause of acute kidney injury (AKI), is associated with a high morbidity and mortality. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is an endogenous detoxifying enzyme. A recombinant human ALP compound, ilofotase alfa, showed no safety or tolerability concerns in a phase 2 trial. Renal function improvement over 28 days was significantly greater in the ilofotase alfa group. Moreover, a significant relative reduction in 28-day all-cause mortality of >40% was observed. A follow-up trial has been designed to confirm these findings.
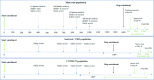
Methods and analysis: This is a phase 3, global, multi-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, sequential design trial in which patients are randomly assigned to either placebo or 1.6 mg/kg ilofotase alfa. Randomisation is stratified by baseline modified Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (mSOFA) score and trial site. The primary objective is to confirm the survival benefit with ilofotase alfa by demonstrating a reduction in 28-day all-cause mortality in patients with sepsis-associated AKI requiring vasopressors. A maximum of 1400 patients will be enrolled at ∼120 sites in Europe, North America, Japan, Australia and New Zealand. Up to four interim analyses will take place. Based on predefined decision rules, the trial may be stopped early for futility or for effectiveness. In addition, patients with COVID-19 disease and patients with 'moderate to severe' chronic kidney disease are analysed as 2 separate cohorts of 100 patients each. An independent Data Monitoring Committee evaluates safety data at prespecified intervals throughout the trial.
Ethics and dissemination: The trial is approved by relevant institutional review boards/independent ethics committees and is conducted in accordance with the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, guidelines of Good Clinical Practice, Code of Federal Regulations and all other applicable regulations. Results of this study will determine the potential of ilofotase alfa to reduce mortality in critically ill patients with sepsis-associated AKI and will be published in a peer-reviewed scientific journal.
Trial registration number: EudraCT CT Number 2019-0046265-24. US IND Number 117 605 Pre-results.
Clinicaltrials: gov number: NCT04411472.
Keywords: COVID-19; acute renal failure; intensive & critical care; nephrology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: PP received advisory board consultancy and travel reimbursements from AM-Pharma. DCA and CJD serve as advisory board consultants for AM-Pharma. JA, EvdB and JB are employees of AM-Pharma. RB, MB, KD, BF, JAK, P-FL, VP and PY received advisory board consultancy reimbursements from AM Pharma. KB worked as an employee of Berry Consultants KB and acted as a consultant to numerous pharmaceutical and device companies. KB is currently an employee of and holds stock in AstraZeneca. JC, ALK and SR are consultants to AM-Pharma. RF received advisory board consultancy reimbursements from AM Pharma and additional consulting reimbursements from BioMerieux, Baxter, Pfizer, MSD, Gilead, Shionogi, Grifols and Beckton Dickinson unrelated to the current study. MJ received advisory board consultancy reimbursements from AM Pharma, additional consulting reimbursement from Baxter and Gilead and grant support from Fresenius and Baxter, unrelated to the current study. KL received advisory board consultancy reimbursements from AM-Pharma, owns stock in Amgen and consultant for Biomerieux, Neumora, Seastar and BOA Medical. RLM received advisory board consultancy reimbursements from AM Pharma and additional consulting reimbursement from BioMerieux, Baxter, Nova Biomed, Abiomed, GE Healthcare, Medtronic, Sanofi and Mallinckrodt, unrelated to the current study. PTM received Trial Steering Committee consultancy payments from AM-Pharma. Other consultancy payments: FAST Biomedical, Novartis, Renibus Therapeutics. MO received speaker honoraria from Fresenius Medical Care, Biomerieux, Baxter and Gilead, and research funding from Fresenius Medical Care, Biomerieux, Baxter and LaJolla Pharma and advisory board consultancy reimbursements from AM-Pharma. AZ received advisory board consultancy reimbursements from AM-Pharma. AZ has received consulting and/or lecture fees from Astute Medical/BioMerieux, Fresenius, Paion, Guard Therapeutics, and Baxter, unrelated to the current study. AZ has received grant support from Astute Medical/BioMerieux, Fresenius and Baxter, unrelated to the current study.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
