Incomplete hippocampal inversion in patients with mutations in genes involved in sonic hedgehog signaling
- PMID: 37012904
- PMCID: PMC10066535
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14712
Incomplete hippocampal inversion in patients with mutations in genes involved in sonic hedgehog signaling
Abstract
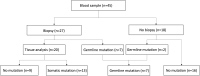
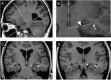
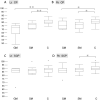
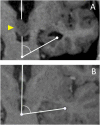
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathways are known to play an important role in the morphological development of the hippocampus in vivo, but their actual roles in humans have not been clarified. Hypothalamic hamartoma (HH) is known to be associated with germline or somatic gene mutations of Shh signaling. We hypothesized that patients with HH and mutations of Shh-related genes also show hippocampal maldevelopment and an abnormal hippocampal infolding angle (HIA). We analyzed 45 patients (age: 1-37 years) with HH who underwent stereotactic radiofrequency thermocoagulation and found Shh-related gene mutations in 20 patients. In addition, 44 pediatric patients without HH (age: 2-25 years) who underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations under the same conditions during the same period were included in this study as a control group. HIA evaluated on MRI was compared between patients with gene mutations and the control group. The median HIA at the cerebral peduncle slice in patients with the gene mutation was 74.36° on the left and 76.11° on the right, and these values were significantly smaller than the corresponding values in the control group (80.46° and 80.56°, respectively, p < 0.01). Thus, mutations of Shh-related genes were correlated to incomplete hippocampal inversion. The HIA, particularly at the cerebral peduncle slice, is a potential indicator of abnormalities of the Shh-signaling pathway.
Keywords: Genetic mutation; Hippocampal infolding angle; Hippocampal inversion; Hypothalamic hamartoma; Sonic hedgehog.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mutations of the Sonic Hedgehog Pathway Underlie Hypothalamic Hamartoma with Gelastic Epilepsy.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Aug 4;99(2):423-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.05.031. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27453577 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of hippocampal infolding angle and incomplete hippocampal inversion in pediatric patients with epilepsy and febrile seizures.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2017 Jul-Aug;23(4):326-330. doi: 10.5152/dir.2017.160077. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28509667 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic mutations in GLI3 and OFD1 involved in sonic hedgehog signaling cause hypothalamic hamartoma.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2016 Mar 24;3(5):356-65. doi: 10.1002/acn3.300. eCollection 2016 May. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27231705 Free PMC article.
-
Brain mosaicism of hedgehog signalling and other cilia genes in hypothalamic hamartoma.Neurobiol Dis. 2023 Sep;185:106261. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106261. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Neurobiol Dis. 2023. PMID: 37579995 Review.
-
Sonic Hedgehog Is a Member of the Hh/DD-Peptidase Family That Spans the Eukaryotic and Bacterial Domains of Life.J Dev Biol. 2018 Jun 8;6(2):12. doi: 10.3390/jdb6020012. J Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29890674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barsi P., Kenéz J., Solymosi D., Kulin A., Halász P., Rásonyi G., Janszky J., Kalóczkai A., Barcs G., Neuwirth M., Paraicz E., Siegler Z., Morvai M., Jerney J., Kassay M., Altmann A. Hippocampal malrotation with normal corpus callosum: a new entity? Neuroradiology. 2000;42(5):339–345. doi: 10.1007/s002340050895. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

