Severe mitral regurgitation in chronic adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma with granulomatous valvular inflammation
- PMID: 37012923
- PMCID: PMC10066408
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jccase.2022.12.001
Severe mitral regurgitation in chronic adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma with granulomatous valvular inflammation
Abstract
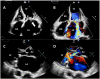
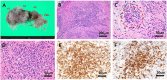
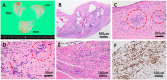
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) is a mature peripheral T-cell neoplasm caused by human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-1) infection. Besides the oncogenic property, HTLV-1 causes HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis and certain inflammatory diseases via a complex host immune response to latent virus infection. Cardiac involvement of ATLL is rare, with the majority of cases being disclosed in postmortem autopsy in patients with advanced subtypes. We herein report the case of a 64-year-old female patient with indolent chronic ATLL with severe mitral regurgitation. Although the condition of ATLL was stable, dyspnea on exertion gradually progressed over the course of three years and echocardiography revealed marked thickening of the mitral valve. Finally, the patient experienced hemodynamic collapse with atrial fibrillation and underwent surgical valve replacement. The removed mitral valve was grossly edematous and swollen. A histological examination revealed a granulomatous reaction mimicking the active phase of rheumatic valvulitis, with the infiltration of ATLL cells that were immunohistochemically positive for CD3, CD4, FoxP3, HLA-DRα, and CCR4. The postoperative course was uneventful, with the exception that Sjögren's syndrome was noted. The history of rheumatic fever was unclear, and such unique valvular pathology was presumably related to autoimmune mechanisms associated with HTLV-1 infection.
Learning objective: We report a case of chronic adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) with isolated valvular infiltration with a unique histology of granulomatous reaction. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I infection may accelerate autoimmune reactions and cardiac inflammation, irrespective of indolent clinical subtype. Among ATLL cases, possible progression of valvular insufficiency and heart failure in patients with cardiac symptoms should be carefully evaluated.
Keywords: Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma; Chronic subtype; Granulomatous valvulitis; Mitral regurgitation; Rheumatic heart disease.
© 2022 Japanese College of Cardiology. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Imaizumi Y., Iwanaga M., Nosaka K., Ishitsuka K., Ishizawa K., Ito S., Amano M., Ishida T., Uike N., Utsunomiya A., Ohshima K., Tanaka J., Tokura Y., Tobinai K., Watanabe T., et al. Prognosis of patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma in Japan: a nationwide hospital-based study. Cancer Sci. 2020;111:4567–4580. - PMC - PubMed
-
- O’Mahony D., Debnath I., Janik J., Aisner D., Jaffe E., Waldmann T., Morris J. Cardiac involvement with human T-cell lymphotrophic virus type-1-associated adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: the NIH experience. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49:439–446. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

