A Prediction Nomogram for Recurrent Retinal Detachment
- PMID: 37013114
- PMCID: PMC10066632
- DOI: 10.2147/RMHP.S403136
A Prediction Nomogram for Recurrent Retinal Detachment
Abstract
Purpose: Recurrent retinal detachment (re-RD) is one of the complications in rhegmatogenous retinal detachment patients who underwent surgical treatment. We investigated the risk factors for re-RD and developed a nomogram for estimating clinical risk.
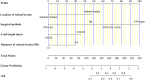
Methods: Univariate and multivariable logistic regression models were performed to determine the association between variables and re-RD, and a nomogram was then developed for re-RD. The nomogram performance was assessed based on its discrimination, calibration, and clinical usefulness.
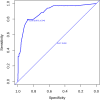
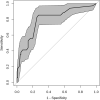
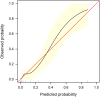
Results: This study analyzed 15 potential variables of re-RD in 403 rhegmatogenous retinal detachment patients who underwent initial surgical treatment. Axial length, inferior breaks, retinal break diameter, and surgical methods were independent risk factors for re-RD. A clinical nomogram incorporating these four independent risk factors was constructed. The diagnostic performance of the nomogram was excellent (area under the curve = 0.892, 95% CI: 0.831-0.953). Our study further validated this nomogram by bootstrapping for 500 repetitions. The area under the curve of the bootstrap model was 0.797 (95% CI: 0.712-0.881). This model showed good calibration curve fitting and a positive net benefit in decision curve analysis.
Conclusion: Axial length, inferior breaks, retinal break diameter, and surgical methods could be risk factors for re-RD. We have developed a prediction nomogram of re-RD for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment following initial surgical treatment.
Keywords: nomogram; recurrent retinal detachment; risk factors.
© 2023 Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nomogram to predict prolonged postoperative ileus after gastrectomy in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Oct 14;25(38):5838-5849. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i38.5838. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31636476 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of Recurrent Retinal Detachment Surgery following Pars Plana Vitrectomy for Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment.Semin Ophthalmol. 2018;33(5):657-663. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2017.1395893. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Semin Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29125779
-
Re-vitrectomy for recurrent retinal detachment in post-vitrectomy eyes of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Nov 16;22(1):439. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02665-8. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36384489 Free PMC article.
-
Tamponade in surgery for retinal detachment associated with proliferative vitreoretinopathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 13;5(5):CD006126. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006126.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32408387 Free PMC article.
-
The Seasonality of Retinal Detachment: Peaks, Troughs, and Global Trends.Life (Basel). 2025 Jan 27;15(2):190. doi: 10.3390/life15020190. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40003599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of gas and silicone oil tamponades for inferior quadrant recurrence in patients undergoing pars plana vitrectomy for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment.Int Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 10;45(1):284. doi: 10.1007/s10792-025-03661-9. Int Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40637769
-
Development and Validation of a Nomogram to Predict the Risk of Special Uterine Leiomyoma Pathological Types or Leiomyosarcoma in Postmenopausal Women: A Retrospective Study.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024 Jun 21;17:1669-1685. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S461773. eCollection 2024. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024. PMID: 38919406 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and risk factors for recurrence after surgical treatment of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: a retrospective cohort study.Int J Retina Vitreous. 2025 May 22;11(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s40942-025-00680-7. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2025. PMID: 40405309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Popovic MM, Muni RH, Nichani P, Kertes PJ. Pars plana vitrectomy, scleral buckle, and pneumatic retinopexy for the management of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: a meta-analysis. Surv Ophthalmol. 2022;67(1):184–196. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg DM, Ghayur HS, Deonarain DM, et al. Supplemental scleral buckle for the management of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment by pars plana vitrectomy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ophthalmologica. 2022;245(2):101–110. - PubMed
-
- Wykoff CC, Schwartz SG, Adelman RA, Brucker AJ, Flynn HW Jr. Primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment repair: evidence supports an individualised approach. Br J Ophthalmol. 2015;99(11):1451–1453. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

