A structure activity relationship study of 3,4'-dimethoxyflavone for ArlRS inhibition in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 37013457
- PMCID: PMC10192164
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ob00123g
A structure activity relationship study of 3,4'-dimethoxyflavone for ArlRS inhibition in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
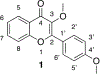
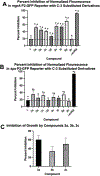
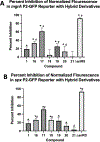
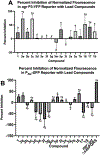
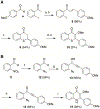
Infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) are difficult to treat due to their resistance to many β-lactam antibiotics, and their highly coordinated excretion of virulence factors. One way in which MRSA accomplishes this is by responding to environmental stimuli using two-component systems (TCS). The ArlRS TCS has been identified as having a key role in regulating virulence in both systemic and local infections caused by S. aureus. We recently disclosed 3,4'-dimethoxyflavone as a selective ArlRS inhibitor. In this study we explore the structure-activity relationship (SAR) of the flavone scaffold for ArlRS inhibition and identify several compounds with increased activity compared to the parent. Additionally, we identify a compound that suppresses oxacillin resistance in MRSA, and begin to probe the mechanism of action behind this activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


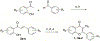
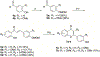
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus ArlRS Two-Component Regulatory System Blocks Virulence.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Jul 19;66(7):e0018722. doi: 10.1128/aac.00187-22. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35736133 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ArlRS in regulating oxacillin susceptibility in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus indicates it is a potential target for antimicrobial resistance breakers.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019;8(1):503-515. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2019.1595984. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019. PMID: 30924407 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ArlRS in autolysis in methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains.J Bacteriol. 2012 Feb;194(4):759-67. doi: 10.1128/JB.06261-11. Epub 2011 Dec 2. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22139508 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the NaHCO3 Transporter MpsABC in the NaHCO3-β-Lactam-Responsive Phenotype in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0014123. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00141-23. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37102972 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Five and Six-Membered Heterocyclic Compounds Targeting the Penicillin-Binding Protein 2 (PBP2A) of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).Molecules. 2023 Oct 10;28(20):7008. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207008. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37894491 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure-Photoreactivity Relationship Study of Substituted 3-Hydroxyflavones and 3-Hydroxyflavothiones for Improving Carbon Monoxide Photorelease.J Org Chem. 2024 Apr 5;89(7):4888-4903. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.4c00070. Epub 2024 Mar 22. J Org Chem. 2024. PMID: 38517741 Free PMC article.
-
Disarming Staphylococcus aureus: Review of Strategies Combating This Resilient Pathogen by Targeting Its Virulence.Pathogens. 2025 Apr 15;14(4):386. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14040386. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40333163 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

