Inflammatory Mechanisms in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
- PMID: 37013947
- PMCID: PMC10396273
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00004.2023
Inflammatory Mechanisms in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract
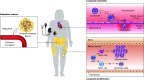
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is now the most common form of heart failure and a significant public health concern for which limited effective therapies exist. Inflammation triggered by comorbidity burden is a critical element of HFpEF pathophysiology. Here, we discuss evidence for comorbidity-driven systemic and myocardial inflammation and the mechanistic role of inflammation in pathological myocardial remodeling in HFpEF.
Keywords: heart failure; inflammation; meta-inflammation; myocardial remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Schiattarella GG, Alcaide P, Condorelli G, Gillette TG, Heymans S, Jones EA, Kallikourdis M, Lichtman A, Marelli-Berg F, Shah S, Thorp EB, Hill JA. Immunometabolic mechanisms of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat Cardiovasc Res 1: 211–222, 2022. doi:10.1038/s44161-022-00032-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

