RBM47 regulates intestinal injury and tumorigenesis by modifying proliferation, oxidative response, and inflammatory pathways
- PMID: 37014710
- PMCID: PMC10243830
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.161118
RBM47 regulates intestinal injury and tumorigenesis by modifying proliferation, oxidative response, and inflammatory pathways
Abstract
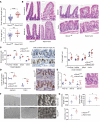
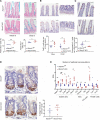
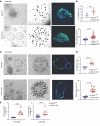
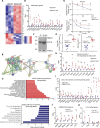
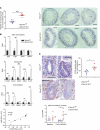
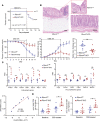
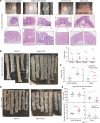
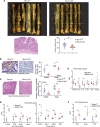
RNA-binding protein 47 (RBM47) is required for embryonic endoderm development, but a role in adult intestine is unknown. We studied intestine-specific Rbm47-knockout mice (Rbm47-IKO) following intestinal injury and made crosses into ApcMin/+ mice to examine alterations in intestinal proliferation, response to injury, and tumorigenesis. We also interrogated human colorectal polyps and colon carcinoma tissue. Rbm47-IKO mice exhibited increased proliferation and abnormal villus morphology and cellularity, with corresponding changes in Rbm47-IKO organoids. Rbm47-IKO mice adapted to radiation injury and were protected against chemical-induced colitis, with Rbm47-IKO intestine showing upregulation of antioxidant and Wnt signaling pathways as well as stem cell and developmental genes. Furthermore, Rbm47-IKO mice were protected against colitis-associated cancer. By contrast, aged Rbm47-IKO mice developed spontaneous polyposis, and Rbm47-IKO ApcMin/+ mice manifested an increased intestinal polyp burden. RBM47 mRNA was decreased in human colorectal cancer versus paired normal tissue, along with alternative splicing of tight junction protein 1 mRNA. Public databases revealed stage-specific reduction in RBM47 expression in colorectal cancer associated independently with decreased overall survival. These findings implicate RBM47 as a cell-intrinsic modifier of intestinal growth, inflammatory, and tumorigenic pathways.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Gastroenterology; Inflammation; RNA processing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apobec1 complementation factor (A1CF) and RBM47 interact in tissue-specific regulation of C to U RNA editing in mouse intestine and liver.RNA. 2019 Jan;25(1):70-81. doi: 10.1261/rna.068395.118. Epub 2018 Oct 11. RNA. 2019. PMID: 30309881 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal epithelial HuR modulates distinct pathways of proliferation and apoptosis and attenuates small intestinal and colonic tumor development.Cancer Res. 2014 Sep 15;74(18):5322-35. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0726. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25085247 Free PMC article.
-
Intestine-Specific Mttp Deletion Increases the Severity of Experimental Colitis and Leads to Greater Tumor Burden in a Model of Colitis Associated Cancer.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 21;8(6):e67819. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067819. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23805328 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding motif protein RBM47 promotes tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through multiple pathways.J Genet Genomics. 2021 Jul 20;48(7):595-605. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2021.05.006. Epub 2021 Jun 15. J Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34274258
-
RNA binding motif 47 (RBM47): emerging roles in vertebrate development, RNA editing and cancer.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Dec;476(12):4493-4505. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04256-5. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34499322 Review.
Cited by
-
RBM47 functions as an anti-oncogene by regulating expression and alternative splicing of cell proliferation and apoptosis associated genes in colorectal cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 22;15(1):26685. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05151-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40695891 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of RNA binding protein 47 predicts low survival in patients and promotes the development of renal cell malignancies through RNA stability modification.Mol Biomed. 2023 Nov 14;4(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s43556-023-00148-w. Mol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37962768 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Insights into Alternative Gene Splicing in Oxidative Stress and Tissue Injury.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2024 Nov;41(13-15):890-909. doi: 10.1089/ars.2023.0437. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2024. PMID: 37776178 Review.
-
Critical gene signature and immunological characterization in peripheral vascular atherosclerosis: novel insights from mendelian randomization and transcriptomics.Front Genet. 2024 Apr 10;15:1361445. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1361445. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38660678 Free PMC article.
-
RBM47 is a novel immunotherapeutic target and prognostic biomarker in gliomas.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 5;15(1):854. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84719-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39757245 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK128169/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106382/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125296/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119437/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK132496/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK105129/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK124274/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA239645/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA246208/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI156236/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK109384/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA230289/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

