GPR84 regulates pulmonary inflammation by modulating neutrophil functions
- PMID: 37016043
- PMCID: PMC10072043
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-023-01080-z
GPR84 regulates pulmonary inflammation by modulating neutrophil functions
Abstract
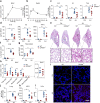
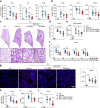
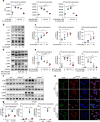
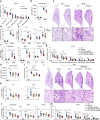
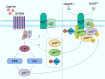
Acute lung injury (ALI) is an acute, progressive hypoxic respiratory failure that could develop into acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) with very high mortality rate. ALI is believed to be caused by uncontrolled inflammation, and multiple types of immune cells, especially neutrophils, are critically involved in the development of ALI. The treatment for ALI/ARDS is very limited, a better understanding of the pathogenesis and new therapies are urgently needed. Here we discover that GPR84, a medium chain fatty acid receptor, plays critical roles in ALI development by regulating neutrophil functions. GPR84 is highly upregulated in the cells isolated from the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of LPS-induced ALI mice. GPR84 deficiency or blockage significantly ameliorated ALI mice lung inflammation by reducing neutrophils infiltration and oxidative stress. Further studies reveal that activation of GPR84 strongly induced reactive oxygen species production from neutrophils by stimulating Lyn, AKT and ERK1/2 activation and the assembly of the NADPH oxidase. These results reveal an important role of GPR84 in neutrophil functions and lung inflammation and strongly suggest that GPR84 is a potential drug target for ALI.
Keywords: GPR84; ROS; acute lung injury; antagonist; inflammation; neutrophil.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
YMZ, employee of Burgeon Therapeutics Co. Ltd, participated in the synthesis of BGT-004. All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A key role for platelet GPVI in neutrophil recruitment, migration, and NETosis in the early stages of acute lung injury.Blood. 2023 Oct 26;142(17):1463-1477. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023019940. Blood. 2023. PMID: 37441848
-
"Rogue" neutrophil-subset [DEspR+CD11b+/CD66b+] immunotype is an actionable therapeutic target for neutrophilic inflammation-mediated tissue injury - studies in human, macaque and rat LPS-inflammation models.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 4;13:1008390. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1008390. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275710 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis-related signature and immune infiltration characterization in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome.Respir Res. 2023 Jun 10;24(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02429-y. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 37301835 Free PMC article.
-
Could Heme Oxygenase-1 Be a New Target for Therapeutic Intervention in Malaria-Associated Acute Lung Injury/Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome?Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 May 16;8:161. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00161. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29868517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of indirect (secondary) acute lung injury.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2011 Feb;5(1):115-26. doi: 10.1586/ers.10.92. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2011. PMID: 21348592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring orphan GPCRs in neurodegenerative diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 4;15:1394516. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1394516. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38895631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycobacteria Exploit Host GPR84 to Dampen Pro-Inflammatory Responses and Promote Infection in Macrophages.Microorganisms. 2025 Jan 8;13(1):110. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13010110. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 39858878 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Nanomaterials Targeting Immune Cells in the Treatment of Chronic Inflammation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Dec 25;19:13925-13946. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S497590. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39735324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic GPR84 Agonists in Colorectal Cancer: Effective in THP-1 Cells but Ineffective in BMDMs and MC38 Mouse Tumor Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 9;26(2):490. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020490. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859206 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbes improve prognosis of Klebsiella pneumoniae pulmonary infection through the lung-gut axis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jun 5;14:1392376. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1392376. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38903943 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

