Cytokines in primary headache disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37016284
- PMCID: PMC10071234
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-023-01572-7
Cytokines in primary headache disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The role of inflammation and cytokines in the pathophysiology of primary headache disorders is uncertain. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to synthesise the results of studies comparing peripheral blood cytokine levels between patients with migraine, tension-type headache, cluster headache, or new daily persistent headache (NDPH), and healthy controls; and in migraine between the ictal and interictal stages.
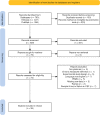
Methods: We searched PubMed/Medline and Embase from inception until July 2022. We included original research studies which measured unstimulated levels of any cytokines in peripheral blood using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay or similar assay. We assessed risk of bias using the Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale. We used random effects meta-analysis with inverse variance weighted average to calculate standardised mean difference (SMD), 95% confidence intervals, and heterogeneity for each comparison. This study is registered with PROSPERO (registration number CRD42023393363). No funding was received for this study.
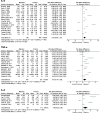
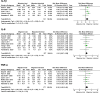
Results: Thirty-eight studies, including 1335 patients with migraine (32 studies), 302 with tension-type headache (nine studies), 42 with cluster headache (two studies), and 1225 healthy controls met inclusion criteria. Meta-analysis showed significantly higher interleukin (IL)-6 (SMD 1.07, 95% CI 0.40-1.73, p = 0.002), tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α (SMD 0.61, 95% CI 0.14-1.09, p = 0.01), and IL-8 (SMD 1.56, 95% CI 0.03-3.09, p = 0.04), in patients with migraine compared to healthy controls, and significantly higher interleukin-1β (IL-1β) (SMD 0.34, 95% CI 0.06-0.62, p = 0.02) during the ictal phase of migraine compared to the interictal phase. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β (SMD 0.52, 95% CI 0.18-0.86, p = 0.003) and TNF-α (SMD 0.64, 95% CI 0.33-0.96, p = 0.0001) were both higher in patients with tension-type headache than controls.
Conclusions: The higher levels of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in migraine compared to controls, and IL-1β during the ictal stage, suggest a role for inflammation in the pathophysiology of migraine, however prospective studies are required to confirm causality and investigate the mechanisms for the increase in cytokine levels identified. Cytokines may also have a role in tension-type headache. Due a lack of data, no conclusions can be made regarding cluster headache or NDPH.
Keywords: Cytokine; Immunology; Migraine disorders; Neurogenic inflammation; Tension-type headache.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AKM has no conflicts of interest.
SC has received a research fellowship sponsored by Abbott.
JR has served on advisory boards for Viatris, Lilly and Pfizer and has received compensation for educational presentations supported by Allergan, Novartis and Viatris.
EH has served on advisory boards for Sanofi-Genzyme, Novartis, Teva, Eli Lilly, Allergan and Lundbeck, been involved in clinical trials sponsored by Novartis,Teva, Xalud, Cerecin, AEON Biopharma and Abbvie and has received payment for educational presentations from Allergan, Teva, Eli Lilly and Novartis.
MM is chair of the medical advisory board of the CSF Leak Association; has served on advisory boards for Allergan, Autonomic Technologies Inc, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Salvia and TEVA; has received payment for educational presentations from Allergan, electroCore, Eli Lilly, Novartis and TEVA; has received grants from Abbott, Medtronic and electroCore; and has a patent on system and method for diagnosing and treating headaches (WO2018051103A1, issued).
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

