Conformationally Controlled sp3 -Hydrocarbon-Based α-Helix Mimetics
- PMID: 37017133
- PMCID: PMC10953326
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202301209
Conformationally Controlled sp3 -Hydrocarbon-Based α-Helix Mimetics
Abstract
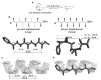
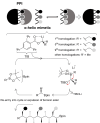
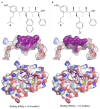
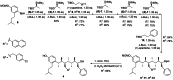
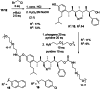
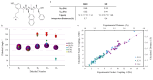
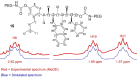
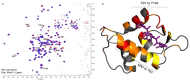
With over 60 % of protein-protein interfaces featuring an α-helix, the use of α-helix mimetics as inhibitors of these interactions is a prevalent therapeutic strategy. However, methods to control the conformation of mimetics, thus enabling maximum efficacy, can be restrictive. Alternatively, conformation can be controlled through the introduction of destabilizing syn-pentane interactions. This tactic, which is often adopted by Nature, is not a common feature of lead optimization owing to the significant synthetic effort required. Through assembly-line synthesis with NMR and computational analysis, we have shown that alternating syn-anti configured contiguously substituted hydrocarbons, by avoiding syn-pentane interactions, adopt well-defined conformations that present functional groups in an arrangement that mimics the α-helix. The design of a p53 mimetic that binds to Mdm2 with moderate to good affinity, demonstrates the therapeutic promise of these scaffolds.
Keywords: Conformation Control; Organoboron; Protein-Protein Interactions; Syn-Pentane Interactions; α-Helix Mimetics.
© 2023 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- None
-
- Jayatunga M. K., Thompson S., Hamilton A. D., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 717; - PubMed
-
- Algar S., Martín-Martínez M., González-Muñiz R., Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 211, 113015; - PubMed
-
- Lenci E., Trabocchi A., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3262; - PubMed
-
- Mabonga L., Kappo A. P., Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 225;
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

