Postexposure Doxycycline to Prevent Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections
- PMID: 37018493
- PMCID: PMC10140182
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2211934
Postexposure Doxycycline to Prevent Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections
Abstract
Background: Interventions to reduce sexually transmitted infections (STIs) among men who have sex with men (MSM) are needed.
Methods: We conducted an open-label, randomized study involving MSM and transgender women who were taking preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection (PrEP cohort) or living with HIV infection (persons living with HIV infection [PLWH] cohort) and who had had Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea), Chlamydia trachomatis (chlamydia), or syphilis in the past year. Participants were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to take 200 mg of doxycycline within 72 hours after condomless sex (doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis) or receive standard care without doxycycline. STI testing was performed quarterly. The primary end point was the incidence of at least one STI per follow-up quarter.
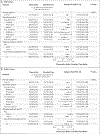
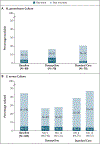
Results: Of 501 participants (327 in the PrEP cohort and 174 in the PLWH cohort), 67% were White, 7% Black, 11% Asian or Pacific Islander, and 30% Hispanic or Latino. In the PrEP cohort, an STI was diagnosed in 61 of 570 quarterly visits (10.7%) in the doxycycline group and 82 of 257 quarterly visits (31.9%) in the standard-care group, for an absolute difference of -21.2 percentage points and a relative risk of 0.34 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.24 to 0.46; P<0.001). In the PLWH cohort, an STI was diagnosed in 36 of 305 quarterly visits (11.8%) in the doxycycline group and 39 of 128 quarterly visits (30.5%) in the standard-care group, for an absolute difference of -18.7 percentage points and a relative risk of 0.38 (95% CI, 0.24 to 0.60; P<0.001). The incidences of the three evaluated STIs were lower with doxycycline than with standard care; in the PrEP cohort, the relative risks were 0.45 (95% CI, 0.32 to 0.65) for gonorrhea, 0.12 (95% CI, 0.05 to 0.25) for chlamydia, and 0.13 (95% CI, 0.03 to 0.59) for syphilis, and in the PLWH cohort, the relative risks were 0.43 (95% CI, 0.26 to 0.71), 0.26 (95% CI, 0.12 to 0.57), and 0.23 (95% CI, 0.04 to 1.29), respectively. Five grade 3 adverse events and no serious adverse events were attributed to doxycycline. Of the participants with gonorrhea culture available, tetracycline-resistant gonorrhea occurred in 5 of 13 in the doxycycline groups and 2 of 16 in the standard-care groups.
Conclusions: The combined incidence of gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis was lower by two thirds with doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis than with standard care, a finding that supports its use among MSM with recent bacterial STIs. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health; DoxyPEP ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT03980223.).
Copyright © 2023 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

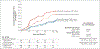
Comment in
-
Doxycycline-PEP - novel and promising but needs monitoring.Nat Rev Urol. 2023 Sep;20(9):522-523. doi: 10.1038/s41585-023-00788-1. Nat Rev Urol. 2023. PMID: 37277465 No abstract available.
-
Postexposure Doxycycline for Sexually Transmitted Infections.N Engl J Med. 2023 Jul 20;389(3):286. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2306480. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37467510 No abstract available.
-
Postexposure Doxycycline for Sexually Transmitted Infections. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2023 Jul 20;389(3):286-287. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2306480. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37467511 No abstract available.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2020. August 22, 2022. (https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2020/default.htm).
-
- Oliver SE, Aubin M, Atwell L, et al. Ocular syphilis — eight jurisdictions, United States, 2014–2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2016;65:1185–8. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2019: Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP) supplement and profiles. July 29, 2021. (https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2019/gisp/docs/GISP_2019_Supplement_e...).
-
- Barbee LA, St Cyr SB. Management of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States: summary of evidence from the development of the 2020 gonorrhea treatment recommendations and the 2021 Centers for Disease Control and prevention sexually transmitted infection treatment guidelines. Clin Infect Dis 2022; 74:Suppl 2:S95–S111. - PubMed
