Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and its fermentation products on growth performance, immune function, intestinal pH, and cecal microorganisms of Lingnan yellow chicken
- PMID: 37019072
- PMCID: PMC10106959
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102610
Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and its fermentation products on growth performance, immune function, intestinal pH, and cecal microorganisms of Lingnan yellow chicken
Abstract
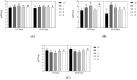
The present research was conducted to investigate the effects of dietary supplementation of Lactobacillus plantarum and its fermentation products on growth performance, specific immune function, intestinal pH, and cecal microorganisms in yellow-feather broilers. A total of 1,200 yellow-feather broilers of similar weight and good health condition at 1 d of age were selected and randomly divided into 5 groups. The CK group was fed the basal diet, and the experimental group (I, II, III, IV) were supplemented with 0.1, 0.15% L. plantarum and 3, 4% L. plantarum fermentation products. The results showed that each treatment could improve the growth performance (P < 0.05) and feed conversion rate of yellow-feather broilers. Besides, the pH value of the gastrointestinal tract of yellow-feather broilers (P < 0.05) was significantly reduced through the use of L. plantarum and its fermentation products as additives, which also facilitated the animals to regulate the balance of cecal microorganisms. The immune function assay showed that the bursal index (P < 0.05), spleen index (P < 0.05), and the content of serum immunoglobulins IgA and IgG (P < 0.05) were significantly increased in yellow-finned broilers aged 1 to 21 d by supplementing the diet with L. plantarum. In conclusion, adding L. plantarum or its fermentation products to the diet can improve the growth performance of yellow-feather broilers, and the direct addition of L. plantarum is better than adding fermentation products.
Keywords: Cecal microorganism; Growth performance; Immune function; Lactobacillus plantarum; Yellow-feather broiler.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Khalaifa H., Al-Nasser A., Al-Surayee T., Al-Kandari S., Al-Enzi N., Al-Sharrah T., Ragheb G., Al-Qalaf S., Mohammed A. Effect of dietary probiotics and prebiotics on the performance of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019;98:4465–4479. - PubMed
-
- Awad W.A., Ghareeb K., Abdel-Raheem S., Böhm J. Effects of dietary inclusion of probiotic and synbiotic on growth performance, organ weights, and intestinal histomorphology of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2009;88:49–56. - PubMed
-
- Blajman J.E., Olivero C.A., Fusari M.L., Zimmermann J.A., Rossler E., Berisvil A.P., Romero Scharpen A., Astesana D.M., Soto L.P., Signorini M.L., Zbrun M.V., Frizzo L.S. Impact of lyophilized Lactobacillus salivarius DSPV 001P administration on growth performance, microbial translocation, and gastrointestinal microbiota of broilers reared under low ambient temperature. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017;114:388–394. - PubMed
-
- Cao G., Tao F., Hu Y., Li Z., Zhang Y., Deng B., Zhan X. Positive effects of a Clostridium butyricum-based compound probiotic on growth performance, immune responses, intestinal morphology, hypothalamic neurotransmitters, and colonic microbiota in weaned piglets. Food Funct. 2019;10:2926–2934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

