Managing respiratory muscle weakness during weaning from invasive ventilation
- PMID: 37019456
- PMCID: PMC10074167
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0205-2022
Managing respiratory muscle weakness during weaning from invasive ventilation
Abstract
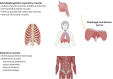
Weaning is a critical stage of an intensive care unit (ICU) stay, in which the respiratory muscles play a major role. Weakness of the respiratory muscles, which is associated with significant morbidity in the ICU, is not limited to atrophy and subsequent dysfunction of the diaphragm; the extradiaphragmatic inspiratory and expiratory muscles also play important parts. In addition to the well-established deleterious effect of mechanical ventilation on the respiratory muscles, other risk factors such as sepsis may be involved. Weakness of the respiratory muscles can be suspected visually in a patient with paradoxical movement of the abdominal compartment. Measurement of maximal inspiratory pressure is the simplest way to assess respiratory muscle function, but it does not specifically take the diaphragm into account. A cut-off value of -30 cmH2O could identify patients at risk for prolonged ventilatory weaning; however, ultrasound may be better for assessing respiratory muscle function in the ICU. Although diaphragm dysfunction has been associated with weaning failure, this diagnosis should not discourage clinicians from performing spontaneous breathing trials and considering extubation. Recent therapeutic developments aimed at preserving or restoring respiratory muscle function are promising.
Copyright ©The authors 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: M. Dres reports personal fees from Lungpacer Med. Inc. for participation to Clinical Advisory Board, research grants, and non-financial support for travel expenses, from Dräger for congress registration (SRLF 2021) and from Bioserenity for research grant, all not related to this work. M. Van Hollebeke and C. Bureau have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures


Comment in
-
New insights into acute and chronic respiratory failure: highlights from the Respiratory Failure and Mechanical Ventilation Conference 2022.Eur Respir Rev. 2023 Apr 5;32(168):230027. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0027-2023. Print 2023 Jun 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2023. PMID: 37019460 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
