Skin Lesion Segmentation in Dermoscopic Images with Noisy Data
- PMID: 37020149
- PMCID: PMC10407008
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-023-00819-8
Skin Lesion Segmentation in Dermoscopic Images with Noisy Data
Abstract
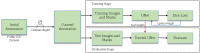
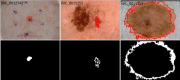
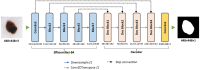
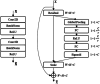
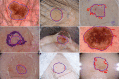
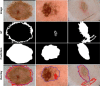
We propose a deep learning approach to segment the skin lesion in dermoscopic images. The proposed network architecture uses a pretrained EfficientNet model in the encoder and squeeze-and-excitation residual structures in the decoder. We applied this approach on the publicly available International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC) 2017 Challenge skin lesion segmentation dataset. This benchmark dataset has been widely used in previous studies. We observed many inaccurate or noisy ground truth labels. To reduce noisy data, we manually sorted all ground truth labels into three categories - good, mildly noisy, and noisy labels. Furthermore, we investigated the effect of such noisy labels in training and test sets. Our test results show that the proposed method achieved Jaccard scores of 0.807 on the official ISIC 2017 test set and 0.832 on the curated ISIC 2017 test set, exhibiting better performance than previously reported methods. Furthermore, the experimental results showed that the noisy labels in the training set did not lower the segmentation performance. However, the noisy labels in the test set adversely affected the evaluation scores. We recommend that the noisy labels should be avoided in the test set in future studies for accurate evaluation of the segmentation algorithms.
Keywords: Deep learning; Dermoscopy; Image segmentation; Melanoma; Noisy data.
© 2023. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, and G. Hinton, ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks, in Advances in Neural Information and Processing Systems (NIPS), vol. 25, 2012, pp. 1097–1105.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

