Effect of plant growth regulators DA-6 and COS on drought tolerance of pineapple through bromelain and oxidative stress
- PMID: 37020215
- PMCID: PMC10074694
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-023-04200-3
Effect of plant growth regulators DA-6 and COS on drought tolerance of pineapple through bromelain and oxidative stress
Abstract
Background: Due to global warming, drought climates frequently occur on land, and despite being drought resistant, pineapples are still subjected to varying degrees of drought stress. Plant growth regulators can regulate the stress tolerance of plants through hormonal effects. This experiment aims to investigate the regulatory effects of different plant growth regulators on Tainong- 16 and MD-2 Pineapple when subjected to drought stress.
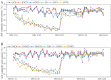
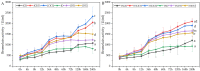
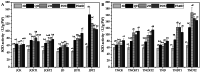
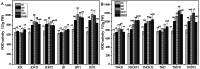
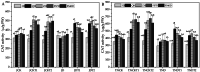
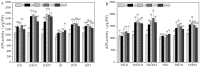
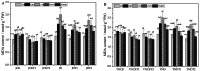
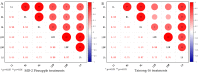
Results: In this experiment, we examined the regulatory effects of two different plant growth regulators, sprayed on two pineapple varieties: MD-2 Pineapple and Tainong-16. The main component of T1 was diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate (DA-6) and that of T2 is chitosan oligosaccharide (COS). An environment similar to a natural drought was simulated in the drought stress treatments. Then, pineapples at different periods were sampled and a series of indicators were measured. The experimental results showed that the drought treatments treated with T1 and T2 plant growth regulators had a decrease in malondialdehyde, an increase in bromelain and antioxidant enzyme indicators, and an increase in phenotypic and yield indicators.
Conclusion: This experiment demonstrated that DA-6 and COS can enhance the drought resistance of pineapple plants to a certain extent through bromelain and oxidative stress. Therefore, DA-6 and COS have potential applications and this experiment lays the foundation for further research.
Keywords: Bromelain; Drought; Oxidative stress; Pineapple; Plant growth regulators.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fractionation and activity profiling of fruit bromelain from pineapples of Phuket variety growing in Thailand.J Food Biochem. 2019 Nov;43(11):e13011. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13011. Epub 2019 Aug 8. J Food Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31393018
-
Ectopic Overexpression of Pineapple Transcription Factor AcWRKY31 Reduces Drought and Salt Tolerance in Rice and Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 3;23(11):6269. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116269. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682951 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and characterization of bromelain from pineapple (Ananas comosus L.) peel waste.J Food Sci. 2021 Feb;86(2):385-393. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15563. Epub 2021 Jan 7. J Food Sci. 2021. PMID: 33415738
-
An Integrated Framework for Drought Stress in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 28;25(17):9347. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179347. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A manipulative interplay between positive and negative regulators of phytohormones: A way forward for improving drought tolerance in plants.Physiol Plant. 2021 Jun;172(2):1269-1290. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13325. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Physiol Plant. 2021. PMID: 33421147 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of ATAC-seq and RNA-seq reveals the dynamics of chromatin accessibility and gene expression in zoysiagrass response to drought.Plant Cell Rep. 2025 Apr 1;44(4):92. doi: 10.1007/s00299-025-03469-y. Plant Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40167783
-
Diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate reprogramed accumulations of organic metabolites associated with water balance and metabolic homeostasis in white clover under drought stress.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Oct 11;15:1430752. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1430752. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39464286 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of AcWRKY31 Increases Sensitivity to Salt and Drought and Improves Tolerance to Mealybugs in Pineapple.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jul 5;13(13):1850. doi: 10.3390/plants13131850. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38999690 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of DA-6 and MC on the growth, physiology, and yield characteristics of soybean.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Mar 10;25(1):304. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06310-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40059163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nations FaAOottU: International Trade Major Tropical Fruits Preliminary Results. 2021. 2022:8–10.
-
- Zahid G, Iftikhar S, Shimira F, Ahmad HM, Kaçar YA. An overview and recent progress of plant growth regulators (PGRs) in the mitigation of abiotic stresses in fruits: a review. Sci Hort. 2022;309:111621. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111621. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

