Six Spain Thymus essential oils composition analysis and their in vitro and in silico study against Streptococcus mutans
- PMID: 37020229
- PMCID: PMC10074788
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-023-03928-7
Six Spain Thymus essential oils composition analysis and their in vitro and in silico study against Streptococcus mutans
Abstract
Background: Streptococcus mutans is a well-known oral pathogen that plays a critical role in the development of dental caries. Many studies have been directed to discover the chemical compounds present in natural products to inhibit the growth and biofilm formation activity of S. mutans. Thymus essential oils exhibit good inhibition on the growth and pathogenesis of S. mutans. However, details about the active compounds in Thymus essential oil and the inhibition mechanism still remain unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the antimicrobial activity of 6 Thymus species (Three samples of Thymus vulgaris, two samples of Thymus zygis, and one sample of Thymus satureioides essential oils) on S. mutans, to identify the potential active components, and to reveal the underlying mechanism.
Methods: The composition of Thymus essential oils was analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. And its antibacterial effect was evaluated based on the bacterial growth, acid production, biofilm formation and genetic expression of virulence factors by S. mutans. Potential active components of the Thymus essential oil were identified using molecular docking and correlation analysis.
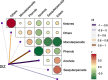
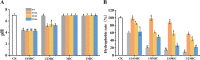
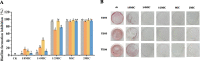
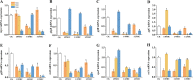
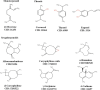
Results: GC-MS analysis showed that the major components in the 6 Spain Thymus essential oils were linalool, α-terpineol, p-cymene, thymol and carvacrol. MIC and MBC analysis showed that 3 Thymus essential oils showed very sensitive antimicrobial activity, and were chosen for further analysis. The 3 Thymus essential oil exhibited a significant inhibitory effect on acid production, adherence and biofilm formation of S. mutans and the expression of virulence genes, such as brpA, gbpB, gtfB, gtfC, gtfD, vicR, spaP and relA. Correlation analysis showed that phenolic components, such as carvacrol and thymol, were positively related to DIZ value, which suggests that they are the potential antimicrobial components. Molecular docking between the Thymus essential oil components and virulence proteins also found that carvacrol and thymol exhibited strong binding affinity with functional domains of virulence genes.
Conclusions: Thymus essential oil showed significant inhibition against the growth and pathogenesis of S. mutans depending on their composition and concentration. And phenolic compounds, such as carvacrol and thymol, are the major active components. Thymus essential oil could be used in oral healthcare products as a potential anti-caries ingredient.
Keywords: Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; Molecular docking; Streptococcus mutans; Thymus essential oil; Virulence factor.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibacterial activity of oregano essential oils against Streptococcus mutans in vitro and analysis of active components.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Feb 21;23(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03890-4. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 36810055 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activity of the essential oil from Lippia sidoides, carvacrol and thymol against oral pathogens.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007 Mar;40(3):349-56. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2007000300010. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007. PMID: 17334532
-
The Inhibitory Effect of Agastache rugosa Essential Oil on the Dental Biofilm.Molecules. 2024 Oct 16;29(20):4907. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204907. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459275 Free PMC article.
-
Thymol, thyme, and other plant sources: Health and potential uses.Phytother Res. 2018 Sep;32(9):1688-1706. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6109. Epub 2018 May 22. Phytother Res. 2018. PMID: 29785774 Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Properties of Thyme Oil and Its Main Constituents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 8;24(8):6936. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086936. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108100 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Plant Oils in Combating Streptococcal Infections: Mechanisms, Efficacy, and Therapeutic Potential.Curr Microbiol. 2025 Aug 18;82(10):460. doi: 10.1007/s00284-025-04438-0. Curr Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40824426 Review.
-
Morphological and genetic diversity assessment of cultivated Thymus satureioides (endemic species) of Morocco.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2025 Mar;23(1):100467. doi: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2025.100467. Epub 2025 Feb 13. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40074441 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Oils for Biofilm Control: Mechanisms, Synergies, and Translational Challenges in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 May 13;14(5):503. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14050503. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40426569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streptococcus mutans biofilms in the establishment of dental caries: a review.3 Biotech. 2025 Mar;15(3):62. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04227-3. Epub 2025 Feb 14. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 39959706 Review.
-
Inhibitory effect of Lonicera japonica flos on Streptococcus mutans biofilm and mechanism exploration through metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 3;15:1435503. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1435503. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39027105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Sugars and dental caries. Geneva: WHO. 2017.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

