Echocardiography parameters used in identifying right ventricle dysfunction in preterm infants with early bronchopulmonary dysplasia: A scoping review
- PMID: 37020655
- PMCID: PMC10067920
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2023.1114587
Echocardiography parameters used in identifying right ventricle dysfunction in preterm infants with early bronchopulmonary dysplasia: A scoping review
Abstract
Background: Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) is a chronic condition that affects preterm infants and is associated with long-term complications. Haemodynamic effects of BPD can lead to right ventricular (RV) dysfunction.
Objective: To synthesise and map the evidence of echo parameters used in identifying RV dysfunction in the first two weeks-after-birth (WAB) of preterm infants with early BPD.
Information sources: This scoping review included the databases: Medline, CINAHL, PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, ProQuest, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, JBI Evidence-Based Practise and Gray Literature.
Search strategy: The search utilised Boolean operators and descriptors registered in Medical Subject Headings.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria: Included were studies utilising echo parameters to examine RV function in preterm infants with early BPD in the first two WAB.
Synthesis of results: The results are presented as a map of the extracted findings in a tabular format with a narrative summary.
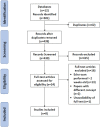
Results: Eight studies were included. Differences were observed in the number and timing of echo scans performed in the first two WAB and the variations in the echo parameters used to compare preterm infants with and without early BPD. Only echo scans performed at the end of the first WAB, demonstrated significant differences in the echo parameters measurements between preterm infants with and without BPD. Studies using RV Myocardial Performance Index (MPI) to identify RV-dysfunction associated with early BPD demonstrated similar findings. The Pulsed-Wave Doppler technique identified differences in RV-MPI between preterm infants with and without BPD, while Tissue-Doppler-Imaging did not demonstrate similar results. Speckle tracking can measure strain (S) and strain rate (SR) and diagnose RV-dysfunction. However, the findings of studies that utilised speckle tracking varied. Finally, two of the included studies added blood tests to their diagnostic model of early BPD, which was able to demonstrate significant differences in blood test results between BPD-affected and control preterm infants.
Conclusion: BPD could adversely affect the myocardium function of the RV; these negative influences can be captured in the first two WAB. However, there are still knowledge gaps regarding the appropriate number, timing and the most suitable echo parameters to assess RV function.
Keywords: bronchopulmonar dysplasia; echocardiogaphy; haemodynamic effects; preterm infants; right ventricular function; scoping review.
© 2023 Muhsen, Nestaas, Hosking and Latour.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Right ventricle speckle tracking in bronchopulmonary dysplasia: one-year follow-up.Egypt Heart J. 2023 Feb 9;75(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s43044-023-00336-7. Egypt Heart J. 2023. PMID: 36757528 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Utility of Echocardiography for Early and Late Pulmonary Hypertension in Preterm Infants: Relation with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2017 Dec;25(4):124-130. doi: 10.4250/jcu.2017.25.4.124. Epub 2017 Dec 29. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2017. PMID: 29333219 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Right Ventricular Systolic Function in Young Adults Born Preterm.Chest. 2021 Jul;160(1):287-296. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2021.01.079. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Chest. 2021. PMID: 33549599
-
A scoping review of echocardiographic and lung ultrasound biomarkers of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants.Front Pediatr. 2023 Feb 10;11:1067323. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1067323. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36846161 Free PMC article.
-
Positive end-expiratory pressure for preterm infants requiring conventional mechanical ventilation for respiratory distress syndrome or bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 26;2(2):CD004500. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004500.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30820939 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Reference ranges of left ventricular diastolic multimodal ultrasound parameters in stable preterm infants in the early and late neonatal intensive care admission period.J Perinatol. 2025 Jul;45(7):920-926. doi: 10.1038/s41372-025-02278-1. Epub 2025 May 17. J Perinatol. 2025. PMID: 40379903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NNAP, National Neonatal Audit Programme, Annual report on 2019 data. 2020, Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials