PPAR- γ Activation Alleviates Osteoarthritis through Both the Nrf2/NLRP3 and PGC-1 α/ Δψ m Pathways by Inhibiting Pyroptosis
- PMID: 37020714
- PMCID: PMC10070030
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/2523536
PPAR- γ Activation Alleviates Osteoarthritis through Both the Nrf2/NLRP3 and PGC-1 α/ Δψ m Pathways by Inhibiting Pyroptosis
Abstract
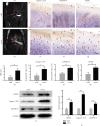
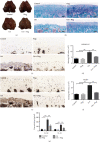
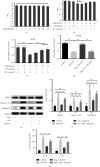
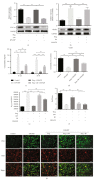
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative joint disease with a gradually increasing morbidity in the aging and obese population. Emerging evidence has implicated pyroptosis in the etiology of OA and it may be recognized as a therapeutic target in OA. We have previously reported regarding another disease that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) activation exerts an anti-inflammatory effect by suppressing the nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain-like receptor containing protein (NLRP) 3 inflammasome. However, the relationship between PPAR-γ and NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis in OA cartilage and its underlying mechanisms is fully unclear. In this study, we found that the level of NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis in severe lateral femoral condyle cartilage wear in the knee of an OA patient was significantly higher than that in the mild lateral femoral condyle cartilage wear areas. Moreover, in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-induced primary chondrocytes and knee OA rat models, we demonstrated that activation of PPAR-γ by pioglitazone (Piog) attenuated LPS/ATP-induced chondrocyte pyroptosis and arthritis. These effects were partially counteracted by either blocking the nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor (Nrf2)/NLRP3 or PGC1-α/Δψ m signaling pathway. Simultaneous depression of these two signaling pathways can completely abrogate the protective effects of Piog on OA and chondrocytes. Taken together, Piog protects OA cartilage against pyroptosis-induced damage by simultaneously activating both the Nrf2/NLRP3 and PGC-1α/Δψ m pathways, which enhances antioxidative and anti-inflammatory responses as well as mitochondrial biogenesis. Therefore, Piog may be a promising agent for human OA cartilage damage in future clinical treatments.
Copyright © 2023 Zhencheng Feng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare(s) that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The IRF1/GBP5 axis promotes osteoarthritis progression by activating chondrocyte pyroptosis.J Orthop Translat. 2023 Dec 29;44:47-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2023.11.005. eCollection 2024 Jan. J Orthop Translat. 2023. PMID: 38229660 Free PMC article.
-
Activating Nrf2 signalling alleviates osteoarthritis development by inhibiting inflammasome activation.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Nov;24(22):13046-13057. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15905. Epub 2020 Sep 23. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32965793 Free PMC article.
-
Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2019 Sep 11;14(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1307-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31511005 Free PMC article.
-
PGC-1α in osteoarthritic chondrocytes: From mechanism to target of action.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 6;14:1169019. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1169019. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37089944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The role of chondrocyte mitochondrial biogenesis in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Feb 15;36(2):242-248. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202109091. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35172413 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
BRD4 promotes gouty arthritis through MDM2-mediated PPARγ degradation and pyroptosis.Mol Med. 2024 May 21;30(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00831-w. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38773379 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound therapy inhibits knee osteoarthritis progression in rabbits by activating the PPARs pathway: a pilot study.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2537348. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2537348. Epub 2025 Jul 25. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40708540 Free PMC article.
-
Pyroptosis: A spoiler of peaceful coexistence between cells in degenerative bone and joint diseases.J Adv Res. 2025 May;71:227-262. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.06.010. Epub 2024 Jun 13. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38876191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress as a key modulator of cell fate decision in osteoarthritis and osteoporosis: a narrative review.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Sep 30;28(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00489-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37777764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyroptosis-related crosstalk in osteoarthritis: Macrophages, fibroblast-like synoviocytes and chondrocytes.J Orthop Translat. 2024 Jun 29;47:223-234. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.06.014. eCollection 2024 Jul. J Orthop Translat. 2024. PMID: 39040491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boileau C., Martel-Pelletier J., Moldovan F., et al. The in situ up-regulation of chondrocyte interleukin-1–converting enzyme and interleukin-18 levels in experimental osteoarthritis is mediated by nitric oxide. Arthritis and Rheumatism . 2002;46(10):2637–2647. doi: 10.1002/art.10518. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

