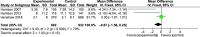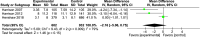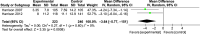The Effect of Motivational Interviewing on Reduction of New Carious Lesions in Children with Early Childhood Caries: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 37020773
- PMCID: PMC10067999
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2497
The Effect of Motivational Interviewing on Reduction of New Carious Lesions in Children with Early Childhood Caries: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Preventive therapies rely on effective behavior change. Motivational interviewing (MI), has been the most recent advancement in behavior therapies that have been successful in tobacco cessation. The effectiveness of MI needs to be evaluated in caries prevention.
Objectives: To evaluate the effectiveness of MI on the reduction of new carious lesions in children with early childhood caries (ECC).
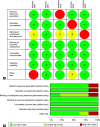
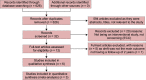
Materials and methods: The two authors independently searched data from Cochrane Library, PubMed, Google Scholar, J gate, and Quintpub. Selection criteria-interventional studies written in the English language with MI as an intervention, a mean follow-up period of atleast 2 years, ECC with decayed, missing, and filled primary teeth/decayed, missing, and filled primary surfaces (dmft/dmfs) as the outcome measures, in the age group of 0-6 years. We excluded cross-sectional studies. Information regarding methods, participants, interventions, outcome measures, and results were extracted. A risk of bias assessment within and across studies was conducted. Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) criteria were applied to generate quality evidence.
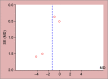
Results: Six studies with a total of 2,663 participants were included in the review, and meta-analysis was conducted on 4; 3 studies had a high risk of bias. A mean reduction of 2.16 (-5.06, 0.75) was observed with MI as an intervention. A sensitivity analysis revealed a mean reduction of 3.64 (-5.77, -1.51) in favor of MI.
Conclusion: There is some evidence with moderate certainty that MI is beneficial in the reduction of new carious lesions in children with ECC.
How to cite this article: Manek S, Jawdekar AM, Katre AN. The Effect of Motivational Interviewing on Reduction of New Carious Lesions in Children with Early Childhood Caries: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2023;16(1):112-123.
Keywords: Behavior change; Early childhood caries; Motivation interviewing; Oral health behavior.
Copyright © 2023; The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Bagramian RA, Garcia-Godoy F, Volpe AR. The global increase in dental caries. A pending public health crisis. Am J Dent. 2009;22(1):3–8. - PubMed
-
- Freudenthal JJ, Bowen DM. Motivational interviewing to decrease parental risk-related behaviors for early childhood caries. J Dent Hyg. 2010;84(1):29–34. - PubMed
-
- Reza M, Amin MS, Sgro A, et al. Oral health status of immigrant and refugee children in North America: a scoping review. J Can Dent Assoc. 2016;8(g3):1488–2159. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources