Prevalence and management of severe asthma in the Nordic countries: findings from the NORDSTAR cohort
- PMID: 37020835
- PMCID: PMC10068510
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00687-2022
Prevalence and management of severe asthma in the Nordic countries: findings from the NORDSTAR cohort
Abstract
Background: Real-life evidence on prevalence and management of severe asthma is limited. Nationwide population registries across the Nordic countries provide unique opportunities to describe prevalence and management patterns of severe asthma at population level. In nationwide register data from Sweden, Norway and Finland, we examined the prevalence of severe asthma and the proportion of severe asthma patients being managed in specialist care.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study based on the Nordic Dataset for Asthma Research (NORDSTAR) research collaboration platform. We identified patients with severe asthma in adults (aged ≥18 years) and in children (aged 6-17 years) in 2018 according to the European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society definition. Patients managed in specialist care were those with an asthma-related specialist outpatient contact (only available in Sweden and Finland).
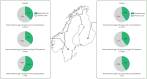
Results: Overall, we identified 598 242 patients with current asthma in Sweden, Norway and Finland in 2018. Among those, the prevalence of severe asthma was 3.5%, 5.4% and 5.2% in adults and 0.4%, 1.0%, and 0.3% in children in Sweden, Norway and Finland, respectively. In Sweden and Finland, 37% and 40% of adult patients with severe asthma and two or more exacerbations, respectively, were managed in specialist care; in children the numbers were 56% and 41%, respectively.
Conclusion: In three Nordic countries, population-based nationwide data demonstrated similar prevalence of severe asthma. In children, severe asthma was a rare condition. Notably, a large proportion of patients with severe asthma were not managed by a respiratory specialist, suggesting the need for increased recognition of severe asthma in primary care.
Copyright ©The authors 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The work was financially supported by Novartis and Sanofi & Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. S. Hansen reports no conflicts of interest. A. von Bülow reports consulting fees from Novartis, speaker fees from Novartis, GSK and AstraZeneca, travel grants from AstraZeneca, and participation in advisory boards with AstraZeneca and Novartis. P. Sandin has no conflicts of interest. O. Ernstsson has no conflicts of interest. C. Janson reports speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, Novartis, Orion Pharma and Sanofi, and expert testimony payments from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, Novartis, Orion Pharma and Sanofi. L. Lehtimäki reports consulting fees from AstraZeneca and GSK, and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, Novartis, Orion Pharma and Sanofi. H. Kankaanranta reports consulting fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, Chiesi, MSD, Orion Pharma, Novartis and Sanofi Genzyme, and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, Chiesi, Mundipharma, Orion Pharma and Sanofi Genzyme. C. Ulrik reports grants from Sanofi, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca and Novartis, consulting fees from Orion Pharma, AstraZeneca and Teva, and participation in advisory boards with Novartis, GSK, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Chiesi and Boehringer Ingelheim. B.B. Aarli reports consulting fees from GSK and AstraZeneca, lecture fees from GSK, AstraZeneca, Sanofi-Aventis Norge, Novartis and Boehringer Ingelheim, and participation in advisory boards with GSK, Astra Zeneca and Sanofi-Aventis Norge. H. Fues Wahl has no conflicts of interest. K. Geale is a board member of Quantify Research AB, Quantify Research ApS, Quantify Research AS and Quantify HEOR Private Limited, is CEO of Quantify Research AB, Quantify Research ApS and Quantify Research AS, and has stock and stock options in Quantify Research AB. S.T. Tang is an employee at Sanofi and holds stocks in Sanofi. M. Wolf is an employee at Novartis Finland. T. Larsen is an employee at Novartis Norway. A. Altraja reports consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK and Sanofi, speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Berlin-Chemie Menarini, Boehringer Ingelheim, Norameda (Chiesi), GSK, Sanofi, Teva and Zentiva, expert testimony for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK and Sanofi, travel grants from AstraZeneca, Berlin-Chemie Menarini, Boehringer Ingelheim and Norameda (Chiesi), participation in advisory boards with AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK and Sanofi, and receipt of equipment from Berlin-Chemie Menarini. H. Backman reports speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK and Sanofi. M. Kilpeläinen reports no conflicts of interest. A. Viinanen reports consulting fees from GSK, speaker fees from AstraZeneca, ALK, GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim and Chiesi, and travel grants from AstraZeneca, Sanofi and Boehringer Ingelheim. D. Ludviksdottir reports travel grants from GSK and AstraZeneca. P. Kauppi reports no conflicts of interest. A. Sverrild reports grants from AstraZeneca, consulting fees from Novartis, speaker fees from AstraZeneca and Chiesi, travel grants from Teva, and participation in advisory boards with Chiesi and Sanofi-Genzyme. S. Lehmann reports no conflicts of interest. V. Backer reports no conflicts of interest. V. Yasinska reports lecture fees from GSK and Sanofi, and participation in advisory boards with AstraZeneca, Chiesi and GSK. T. Skjold reports no conflicts of interest. J. Karjalainen reports consulting fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, MSD and Novartis, and lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, MSD, MundiPharma, Novartis and Orion Pharma. A. Bossios reports lecture fees from GSK, AstraZeneca, Teva and Novartis, travel grants from AstraZeneca and Novartis, and participation in advisory boards with GSK, AstraZeneca, Teva, Novartis and Sanofi, and is a member of the steering committee of SHARP, Secretary of Assembly 5 (Airway diseases, asthma, COPD and chronic cough) of the European Respiratory Society and the vice-president of the Nordic Severe Asthma Network. C. Porsbjerg reports grants from AstraZeneca, GSK, Novartis, Teva, Sanofi, Chiesi and ALK, consulting fees from AZ, GSK, Novartis, TEVA, Sanofi, Chiesi and ALK, lecture fees from AZ, GSK, Novartis, TEVA, Sanofi, Chiesi and ALK, and participation in advisory boards with AstraZeneca, Novartis, TEVA, Sanofi and ALK.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Severe asthma trajectories in adults: findings from the NORDSTAR cohort.Eur Respir J. 2023 Sep 9;62(3):2202474. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02474-2022. Print 2023 Sep. Eur Respir J. 2023. PMID: 37620041 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic airway diseases: basic science, clinical manifestations and future challenges.Eur Clin Respir J. 2022 Mar 2;9(1):2040707. doi: 10.1080/20018525.2022.2040707. eCollection 2022. Eur Clin Respir J. 2022. PMID: 35251534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prevalence of severe asthma and low asthma control among Danish adults.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014 Nov-Dec;2(6):759-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2014.05.005. Epub 2014 Jul 25. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014. PMID: 25439368
-
Patterns of finasteride use in the male populations of four Nordic countries: A cross-national drug utilization study.Scand J Urol. 2016 Jun;50(3):220-7. doi: 10.3109/21681805.2015.1136676. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Scand J Urol. 2016. PMID: 26901820
-
Nordic consensus statement on the systematic assessment and management of possible severe asthma in adults.Eur Clin Respir J. 2018 Mar 6;5(1):1440868. doi: 10.1080/20018525.2018.1440868. eCollection 2018. Eur Clin Respir J. 2018. PMID: 29535852 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Healthcare Resource Utilisation of Severe Uncontrolled T2low and Non-T2low Asthma in Finland During 2018-2021.J Asthma Allergy. 2024 Jul 19;17:681-691. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S455911. eCollection 2024. J Asthma Allergy. 2024. PMID: 39050030 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Treatment Response in Patients With Severe Asthma Using Visual and Quantitative Analysis of Chest CT.Korean J Radiol. 2024 Jul;25(7):673-683. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2024.0110. Korean J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38942461 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Effectiveness of Omalizumab Treatment in Adult Asthma Patients.Yonsei Med J. 2025 Sep;66(9):545-555. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2024.0320. Yonsei Med J. 2025. PMID: 40873141 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of severe asthma in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Respir Rev. 2024 Oct 9;33(174):240095. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0095-2024. Print 2024 Oct. Eur Respir Rev. 2024. PMID: 39384302 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Adipokine Status and Leptin Receptor Gene Polymorphism in Patients with Severe Asthma.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 1;15(9):1154. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15091154. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361972 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
