Efficacy and Safety of Anti-Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Monoclonal Antibody Socazolimab With Carboplatin and Etoposide for Extensive-Stage SCLC: Results From the Phase 1b Clinical Trial
- PMID: 37020926
- PMCID: PMC10067846
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2023.100478
Efficacy and Safety of Anti-Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Monoclonal Antibody Socazolimab With Carboplatin and Etoposide for Extensive-Stage SCLC: Results From the Phase 1b Clinical Trial
Abstract
Introduction: The study (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04346914) is an open label, single-arm, phase 1b clinical trial investigating the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of the recombinant human anti-programmed death-ligand 1 monoclonal antibody socazolimab in combination with carboplatin and etoposide in the first-line treatment of extensive-stage SCLC. Good safety and efficacy were found in previous phase 1 clinical trials of other cancers, such as cervix cancer.
Methods: Patients received socazolimab (5 mg/kg) every three weeks until disease progression or physician decision. Carboplatin (area under the curve: 5) was also administered every three weeks and etoposide (100 mg/m2) on days 1, 2, and 3 of the treatment cycle. The primary purpose of the study was safety measured by the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. Secondary purposes included objective response rate, progression-free survival, duration of response, and overall survival.
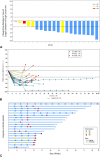
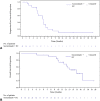
Results: From April 15, 2020 (enrollment date), to December 30, 2021 (data cutoff), 20 patients with extensive-stage SCLC were administered with socazolimab, carboplatin, and etoposide. Objective response rate was 70.0% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 45.72%-88.11%). Median progression-free survival was 5.65 months (95% CI: 4.14-6.54), and the median duration of response was 4.29 months (95% CI: 2.76-5.85). Median overall survival was 14.88 months (95% CI: 10.09-not evaluated). The highest incidence of treatment-related adverse events included anemia (100%), decreased neutrophil count (95%), decreased platelet count (95%), and decreased white blood cell count (95%), which occurred during combination therapy. The most common grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events were neutropenia (90%), decreased white blood cell count (65%), decreased platelet count (50%), and anemia (30%), which were also common adverse reactions of chemotherapy. No adverse events leading to death had occurred.
Conclusions: Results revealed that the combination therapy of socazolimab, carboplatin, and etoposide had preliminarily confirmed the safety of socazolimab in the first-line treatment of SCLC combined with EC chemotherapy. Currently, a phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04878016) is being conducted with 498 patients.
Keywords: Carboplatin; Etoposide; Extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC); PD-L1; Socazolimab.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- Howlader N., Noone A.M., Krapcho M., et al. SEER cancer statistics review (CSR), 1975–2014. National Cancer Institute. Accessed May 2, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2014
-
- Govindan R., Page N., Morgensztern D., et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4539–4544. - PubMed
-
- Jett J.R., Schild S.E., Kesler K.A., Kalemkerian G.P. Treatment of small cell lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer. 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(suppl):e400S–e419S. - PubMed
-
- Evans W.K., Shepherd F.A., Feld R., Osoba D., Dang P., Deboer G. VP-16 and cisplatin as first-line therapy for small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1985;3:1471–1477. - PubMed
-
- Schiller J.H., Adak S., Cella D., DeVore R.F., Johnson D.H. Topotecan versus observation after cisplatin plus etoposide in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: E7593—a phase III trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:2114–2122. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

