NovoSorb Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix for Reconstruction of Multiplanar Degloving Injury of the Upper Limb
- PMID: 37020984
- PMCID: PMC10069825
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004909
NovoSorb Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix for Reconstruction of Multiplanar Degloving Injury of the Upper Limb
Abstract
Originally described as "wringer injuries" by MacCollum in 1938,1 traumatic multiplanar degloving injuries that occur as the result of the hand, forearm or arm being drawn between the rollers of a machine are functionally devastating and present a significant reconstructive challenge. Revascularization and comprehensive excision of devitalized bone and soft tissue, followed by appropriate skeletal fixation and vascularized soft tissue cover are the mainstays of management. To date, published case series have described local flaps and free tissue transfer for coverage of wounds that involve exposed vital structures such as nerves, vessels, and tendons.2 NovoSorb biodegradable temporizing matrix (BTM; PolyNovo Biomaterials Pty Ltd, Melbourne, Australia) is a bilayer bioabsorbable synthetic polymer dermal substitute, which has the ability to integrate into large wound beds and is resistant to infection.3 BTM comprises a bioabsorbable, polyurethane matrix that allows for cellular infiltration and a temporary nonbiodegradable, nonporous polyurethane layer, which limits moisture loss and provides a barrier to bacteria. Here we describe the successful use of BTM in the staged reconstruction of a high-energy industrial roller injury in an adolescent patient.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures


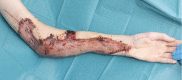
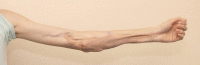
References
-
- MacCollum D. Wringer arm – a report of twenty-six cases. N Engl J Med. 1938;218:549–552.
-
- Greenwood JE, Schmitt BJ, Wagstaff MJD. Experience with a synthetic bilayer biodegradable temporising matrix in significant burn injury. Burns Open. 2018;2:17–34.
-
- Schmitt B, Heath K, Kurmis R, et al. . Early physiotherapy experience with a biodegradable polyurethane dermal substitute: therapy guidelines for use. Burns. 2021;47:1074–1083. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
