Prognostic benefit of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in heart failure: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 37021020
- PMCID: PMC10068943
- DOI: 10.1002/joa3.12812
Prognostic benefit of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in heart failure: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: The prognostic role of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients with heart failure (HF) remains uncertain, with guideline recommendations largely based on a single trial. We conducted a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) assessing the prognostic impact of AF ablation in patients with HF.
Methods: Electronic databases were searched for RCTs comparing 'AF ablation' versus 'other care' (medical therapy and/or atrioventricular node ablation with pacing) in patients with HF. Primary endpoints were ≥1-year mortality, HF hospitalization and change in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). Meta-analyses were performed using random-effects modelling.
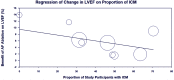
Results: Nine RCTs (n = 1462) met inclusion criteria. Compared to 'other care', AF ablation significantly reduced ≥1-year mortality (relative risk [RR] 0.65; 95% confidence intervals [CI], 0.49-0.87) and HF hospitalization (RR 0.64; 95% CI, 0.51-0.81). AF ablation demonstrated significantly greater improvement in LVEF (mean difference [MD] 5.4; 95% CI, 4.4-6.4), 6-min walk test distance (MD 21.5 meters; 95% CI, 4.6-38.4) and quality of life as measured by Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire score (MD 7.2; 95% CI, 2.8-11.7). Meta-regression analyses showed the beneficial impact of AF ablation on LVEF was significantly blunted by higher prevalence of ischaemic cardiomyopathy.
Conclusions: Our meta-analysis demonstrates AF ablation is superior to 'other care' in improving mortality, HF hospitalization, LVEF and quality of life in patients with HF. However, the highly selected study populations in included RCTs and effect modification mediated by etiology of HF suggests these benefits do not uniformly apply across the HF population.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; catheter ablation; heart failure; meta‐analysis.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Arrhythmia published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Heart Rhythm Society.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Efficacy of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in heart failure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Oct;11(5):2684-2693. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14814. Epub 2024 Apr 25. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38661235 Free PMC article.
-
Catheter Ablation Versus Medical Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials.Heart Lung Circ. 2019 May;28(5):707-718. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2018.10.022. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Heart Lung Circ. 2019. PMID: 30509786 Review.
-
Catheter Ablation versus Medical Therapy of Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Heart Failure: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 21;11(19):5530. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195530. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233407 Free PMC article.
-
Catheter Ablation Compared with Medical Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation with Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 21;18(6):1325-1331. doi: 10.7150/ijms.52257. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33628087 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of catheter ablation vs. medical treatment for atrial fibrillation and heart failure: a meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 May 10;10:1165011. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1165011. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37234370 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Redundant Meta-Analyses on Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Heart Failure.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Nov 21;25(11):418. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2511418. eCollection 2024 Nov. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39618855 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of rhythm versus rate control of atrial fibrillation in heart failure subgroups: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2024 Nov-Dec;24(6):321-329. doi: 10.1016/j.ipej.2024.09.004. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2024. PMID: 39270779 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chiang C‐E, Naditch‐Brûlé L, Murin J, Goethals M, Inoue H, O'Neill J, et al. Distribution and risk profile of paroxysmal, persistent, and permanent atrial fibrillation in routine clinical practice: insight from the real‐life global survey evaluating patients with atrial fibrillation international registry. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012;5:632–9. - PubMed
-
- Chiocchini A, Terricabras M, Verma A. Atrial fibrillation ablation in heart failure: what do we know? What can we do? EP Europace. 2021;23:353–61. - PubMed
-
- Wilber DJ, Pappone C, Neuzil P, De Paola A, Marchlinski F, Natale A, et al. Comparison of antiarrhythmic drug therapy and radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2010;303:333–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

