Emerging roles of i-motif in gene expression and disease treatment
- PMID: 37021044
- PMCID: PMC10067743
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1136251
Emerging roles of i-motif in gene expression and disease treatment
Abstract
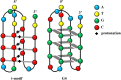
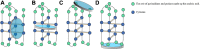
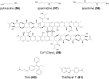
As non-canonical nucleic acid secondary structures consisting of cytosine-rich nucleic acids, i-motifs can form under certain conditions. Several i-motif sequences have been identified in the human genome and play important roles in biological regulatory functions. Due to their physicochemical properties, these i-motif structures have attracted attention and are new targets for drug development. Herein, we reviewed the characteristics and mechanisms of i-motifs located in gene promoters (including c-myc, Bcl-2, VEGF, and telomeres), summarized various small molecule ligands that interact with them, and the possible binding modes between ligands and i-motifs, and described their effects on gene expression. Furthermore, we discussed diseases closely associated with i-motifs. Among these, cancer is closely associated with i-motifs since i-motifs can form in some regions of most oncogenes. Finally, we introduced recent advances in the applications of i-motifs in multiple areas.
Keywords: biological activities; gene-targeted therapy; i-motif; ligand compounds; molecular mechanism; oncogene; telomere.
Copyright © 2023 Luo, Zhang, Gao, Pan, Yang, Li, Chen, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
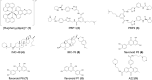


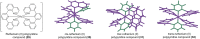


References
-
- Amato J., Iaccarino N., D'Aria F., D'Amico F., Randazzo A., Giancola C., et al. (2022). Conformational plasticity of DNA secondary structures: Probing the conversion between i-motif and hairpin species by circular dichroism and ultraviolet resonance Raman spectroscopies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 24, 7028–7044. 10.1039/d2cp00058j - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

