Zfp580 inactivation as a new therapeutic target to enhance recovery after stroke in mice
- PMID: 37021637
- PMCID: PMC10369148
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X231168499
Zfp580 inactivation as a new therapeutic target to enhance recovery after stroke in mice
Abstract
Paracrine cerebral Interleukin 6 (Il6) is relevant for stroke recovery, but systemic Il6 elevation may worsen outcome. Hence, paracrine Il6 response modulation within the neurovascular unit has emerged as an attractive therapeutic approach. Lithium modulates Il6 responses and improves stroke outcome. However, lithium may cause serious adverse effects. Here, we report that Zincfinger protein 580 (Zfp580) mediates the effects of lithium on Il6 signaling. In contrast to lithium, Zfp580 inactivation had no neurotoxic effects, and Zfp580 knock out mice showed no phenotypic changes in cognitive and motor function behavioral tests. We discovered that lithium and hypoxia disinhibited Il6 via Zfp580 suppression and post-translational modification by small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO). After transient middle cerebral artery occlusion, loss of Zfp580 reduced paracrine Il6 and increased Il6 trans-signaling. Aside from modulating Il6 signaling, Zfp580 loss improved endothelial resilience to ischemia, was highly neuroprotective resulting in smaller infarcts and enhanced use-dependent neuroplasticity, all of which led to improved functional outcome. In conclusion, inactivation of Zfp580 exerts positive effects on multiple key mechanisms without exhibiting relevant adverse side effects, making it potentially a more specific and effective treatment target for stroke recovery than lithium. To fully assess its potential, Zfp580 inhibitors must be developed.
Keywords: Il6 signaling; Zfp580; stroke; stroke recovery; use-dependent plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

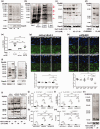


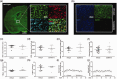

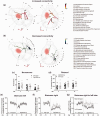
References
-
- Suzuki S, Tanaka K, Suzuki N. Ambivalent aspects of interleukin-6 in cerebral ischemia: inflammatory versus neurotrophic aspects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2009; 29: 464–479. - PubMed
-
- Hunter CA, Jones SA. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat Immunol 2015; 16: 448–457. - PubMed
-
- Rose-John S. The soluble interleukin 6 receptor: Advanced therapeutic options in inflammation. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2017; 102: 591–598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

