Global and national prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adolescents: An analysis of the global burden of disease study 2019
- PMID: 37021791
- PMCID: PMC10521800
- DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000383
Global and national prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adolescents: An analysis of the global burden of disease study 2019
Abstract
Background and aims: NAFLD in adolescents is an increasing health crisis worldwide, but its exact global, continental, and national prevalence, its relationship with other metabolic conditions, and the human development index (HDI) globally are not known.
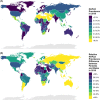
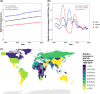
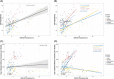
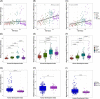
Approach and results: We analyzed data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 to compare global, continental, and national prevalence rates of adolescent NAFLD and associations with other metabolic conditions and HDI. The global NAFLD prevalence in adolescents increased from 3.73% in 1990 to 4.71% in 2019 (a relative increase of 26.27%). The prevalence for the male and female populations was 5.84% and 3.52% in 2019, respectively. The Oceanian and North American continents had the highest adolescent NAFLD prevalence (median: 6.54% and 5.64%, respectively), whereas Europe had the lowest prevalence (median: 3.98%). South America and North America had the highest relative increase in adolescent NAFLD prevalence from 1990 to 2019 (median: 39.25% and 36.87%, respectively). High body mass index and type 2 diabetes mellitus increased significantly in adolescents worldwide. However, only high body mass index and not type 2 diabetes mellitus correlated with NAFLD prevalence in adolescents globally. Countries with a higher HDI had larger increases in adolescent NAFLD prevalence from 1990 to 2019 although countries with the highest HDI (HDI: > 0.9) had the lowest NAFLD prevalence in 2019.
Conclusions: NAFLD in adolescents is an increasing health problem on all continents. Improving environmental factors, including lifestyle but also healthcare policies, can help to prevent NAFLD from developing in children and adolescents and help to improve outcomes in children and adolescents with NAFLD.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Bernd Schnabl consults for Ambys Medicines, Ferring Research Institute, Gelesis, HOST Therabiomics, Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Mabwell Therapeutics, Patara Pharmaceuticals and Takeda. Bernd Schnabl’s institution UC San Diego has received grant support from Artizan Biosciences, Axial Biotherapeutics, BiomX, CymaBay Therapeutics, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Prodigy Biotech and Synlogic Operating Company. The remaining authors have no conflicts to report.
Figures



Comment in
-
Rising tide of NAFLD in youth: A warning bell and call to action.Hepatology. 2023 Oct 1;78(4):1017-1019. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000507. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Hepatology. 2023. PMID: 37278240 No abstract available.
References
-
- Eslam M, Alkhouri N, Vajro P, Baumann U, Weiss R, Socha P, et al. Defining paediatric metabolic (dysfunction)-associated fatty liver disease: an international expert consensus statement. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6:864–73. - PubMed
-
- Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1221–31. - PubMed
-
- Vos MB, Abrams SH, Barlow SE, Caprio S, Daniels SR, Kohli R, et al. NASPGHAN Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Recommendations from the Expert Committee on NAFLD (ECON) and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017;64:319–34. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nobili V, Alisi A, Valenti L, Miele L, Feldstein AE, Alkhouri N. NAFLD in children: new genes, new diagnostic modalities and new drugs. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:517–30. - PubMed

