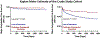Interruption of Insurance Coverage and the Risk of Amputation in Patients with Pre-Existing Commercial Health Insurance and Peripheral Artery Disease
- PMID: 37023922
- PMCID: PMC12244360
- DOI: 10.1016/j.avsg.2023.03.015
Interruption of Insurance Coverage and the Risk of Amputation in Patients with Pre-Existing Commercial Health Insurance and Peripheral Artery Disease
Abstract
Background: Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is linked with an increased risk of lower extremity amputation and multiple socioeconomic factors attenuate this risk. Prior studies have demonstrated increased rates of amputation in PAD patients with suboptimal or no insurance coverage. However, the impact of insurance loss in PAD patients with pre-existing commercial insurance coverage is unclear. In this study, we evaluated the outcomes of PAD patients who lose commercial insurance coverage.
Methods: The Pearl Diver all-payor insurance claims database was used to identify adult patients (>18 years) with a PAD diagnosis from 2010 to 2019. The study cohort included patients with pre-existing commercial insurance and at least 3 years continuous enrollment after diagnosis of PAD. Patients were stratified based on whether they had an interruption of commercial insurance coverage over time. Patients who transitioned from commercial insurance to Medicare and other government-sponsored insurance during follow up were excluded. Adjusted comparison (1:1 ratio) was performed using propensity matching for age, gender, the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), and relevant comorbidities. The main outcomes were major amputation and minor amputation. Cox proportional hazards ratios and Kaplan-Meier estimate were used to examine the association between loss of insurance and outcomes.
Results: Among the 214,386 patients included, 43.3% (n = 92,772) had continuous commercial insurance coverage and 56.7% (n = 121,614) had interruption of coverage (transition to uninsured or Medicaid coverage) during follow up. In the crude cohort and matched cohort, interruption of coverage was associated with lower major amputation-free survival on Kaplan Meier estimate (P < 0.001). In the crude cohort, interruption of coverage was associated with 77% increased risk of major amputation (OR 1.77, 95% CI 1.49-2.12) and a 41% high risk of minor amputation (OR 1.41, 95% CI 1.31-1.53). In the matched cohort, interruption of coverage was associated with 87% increased risk of major amputation (OR 1.87, 95% CI 1.57-2.25) and a 104% increased risk of minor amputation (OR 1.47, 95% CI 1.36-1.60).
Conclusions: Interruption of insurance coverage in PAD patients with pre-existing commercial health insurance was associated with increased risks of lower extremity amputation.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest:
All authors declare no competing interests related to the study.
Figures
References
-
- Regensteiner JG, Hiatt WR, Coll JR, et al. The impact of peripheral arterial disease on health-related quality of life in the Peripheral Arterial Disease Awareness, Risk, and Treatment: New Resources for Survival (PARTNERS) Program. Vasc Med. 2008;13(1):15–24. doi: 10.1177/1358863X07084911 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical