The Tip60/Ep400 chromatin remodeling complex impacts basic cellular functions in cranial neural crest-derived tissue during early orofacial development
- PMID: 37024457
- PMCID: PMC10079831
- DOI: 10.1038/s41368-023-00222-7
The Tip60/Ep400 chromatin remodeling complex impacts basic cellular functions in cranial neural crest-derived tissue during early orofacial development
Abstract
The cranial neural crest plays a fundamental role in orofacial development and morphogenesis. Accordingly, mutations with impact on the cranial neural crest and its development lead to orofacial malformations such as cleft lip and palate. As a pluripotent and dynamic cell population, the cranial neural crest undergoes vast transcriptional and epigenomic alterations throughout the formation of facial structures pointing to an essential role of factors regulating chromatin state or transcription levels. Using CRISPR/Cas9-guided genome editing and conditional mutagenesis in the mouse, we here show that inactivation of Kat5 or Ep400 as the two essential enzymatic subunits of the Tip60/Ep400 chromatin remodeling complex severely affects carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism in cranial neural crest cells. The resulting decrease in protein synthesis, proliferation and survival leads to a drastic reduction of cranial neural crest cells early in fetal development and a loss of most facial structures in the absence of either protein. Following heterozygous loss of Kat5 in neural crest cells palatogenesis was impaired. These findings point to a decisive role of the Tip60/Ep400 chromatin remodeling complex in facial morphogenesis and lead us to conclude that the orofacial clefting observed in patients with heterozygous KAT5 missense mutations is at least in part due to disturbances in the cranial neural crest.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
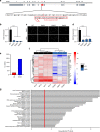



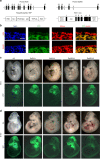


Similar articles
-
Patched1 is required in neural crest cells for the prevention of orofacial clefts.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Dec 15;22(24):5026-35. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt353. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23900075
-
Disruption of DNA methylation-mediated cranial neural crest proliferation and differentiation causes orofacial clefts in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jan 16;121(3):e2317668121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2317668121. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38194455 Free PMC article.
-
Intraflagellar transport 88 (IFT88) is crucial for craniofacial development in mice and is a candidate gene for human cleft lip and palate.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Mar 1;26(5):860-872. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx002. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28069795 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and developmental basis of orofacial clefts.Birth Defects Res. 2020 Nov;112(19):1558-1587. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.1768. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Birth Defects Res. 2020. PMID: 32725806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as epigenetic regulators of orofacial development.Differentiation. 2022 Mar-Apr;124:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2022.01.002. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Differentiation. 2022. PMID: 35144134 Review.
Cited by
-
FBXO24 modulates mRNA alternative splicing and MIWI degradation and is required for normal sperm formation and male fertility.Elife. 2024 Mar 12;12:RP91666. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91666. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38470475 Free PMC article.
-
The multitalented TIP60 chromatin remodeling complex: wearing many hats in epigenetic regulation, cell division and diseases.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2025 Jul 2;18(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13072-025-00603-8. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2025. PMID: 40604793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative regulation of HDAC3 transcription by histone acetyltransferase TIP60 in colon cancer.Genes Genomics. 2024 Jul;46(7):871-879. doi: 10.1007/s13258-024-01524-8. Epub 2024 May 28. Genes Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38805168 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Balance between Transcriptional and Epigenetic Regulation during Developmental Proliferation of Human Cranial Neural Crest Cells.Cells. 2024 Sep 30;13(19):1634. doi: 10.3390/cells13191634. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39404397 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

