Glucocerebrosidase is imported into mitochondria and preserves complex I integrity and energy metabolism
- PMID: 37024507
- PMCID: PMC10079970
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-37454-4
Glucocerebrosidase is imported into mitochondria and preserves complex I integrity and energy metabolism
Abstract
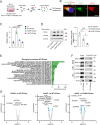
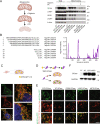
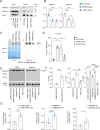
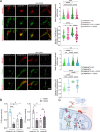
Mutations in GBA1, the gene encoding the lysosomal enzyme β-glucocerebrosidase (GCase), which cause Gaucher's disease, are the most frequent genetic risk factor for Parkinson's disease (PD). Here, we employ global proteomic and single-cell genomic approaches in stable cell lines as well as induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived neurons and midbrain organoids to dissect the mechanisms underlying GCase-related neurodegeneration. We demonstrate that GCase can be imported from the cytosol into the mitochondria via recognition of internal mitochondrial targeting sequence-like signals. In mitochondria, GCase promotes the maintenance of mitochondrial complex I (CI) integrity and function. Furthermore, GCase interacts with the mitochondrial quality control proteins HSP60 and LONP1. Disease-associated mutations impair CI stability and function and enhance the interaction with the mitochondrial quality control machinery. These findings reveal a mitochondrial role of GCase and suggest that defective CI activity and energy metabolism may drive the pathogenesis of GCase-linked neurodegeneration.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

