Diagnostic reference level quantities for adult chest and abdomen-pelvis CT examinations: correlation with organ doses
- PMID: 37024637
- PMCID: PMC10079797
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-023-01403-y
Diagnostic reference level quantities for adult chest and abdomen-pelvis CT examinations: correlation with organ doses
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate correlations between DRL quantities (DRLq) stratified into patient size groups for non-contrast chest and abdomen-pelvis CT examinations in adult patients and the corresponding organ doses.
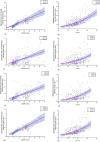
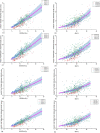
Methods: This study presents correlations between DRLq (CTDIvol, DLP and SSDE) stratified into patient size ranges and corresponding organ doses shared in four groups: inside, peripheral, distributed and outside. The demographic, technical and dosimetric parameters were used to identify the influence of these quantities in organ doses. A robust statistical method was implemented in order to establish these correlations and its statistical significance.
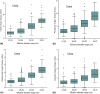
Results: Median values of the grouped organ doses are presented according to the effective diameter ranges. Organ doses in the regions inside the imaged area are higher than the organ doses in peripheral, distributed and outside regions, excepted to the peripheral doses associated with chest examinations. Different levels of statistical significance between organ doses and the DRLq were presented.
Conclusions: Correlations between DRLq and target-organ doses associated with clinical practice can support guidance's to the establishment of optimization criteria. SSDE demonstrated to be significant in the evaluation of organ doses is also highlighted. The proposed model allows the design of optimization actions with specific risk-reduction results.
Keywords: Abdomen-pelvis; Chest; Computed tomography; Organ doses; Statistics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Correlation analysis of organ doses determined by Monte Carlo simulation with dose metrics for patients undergoing chest-abdomen-pelvis CT examinations.Phys Med. 2020 Sep;77:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2020.07.016. Epub 2020 Aug 2. Phys Med. 2020. PMID: 32755745
-
Size-specific dose estimates of adult, chest computed tomography examinations: Comparison of Chinese and updated 2017 American College of Radiology diagnostic reference levels based on the water-equivalent diameter.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 13;16(9):e0257294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257294. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34516579 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing national diagnostic reference levels (DRLs) for computed tomography in Egypt.Phys Med. 2017 Jul;39:16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2017.05.050. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Phys Med. 2017. PMID: 28711184
-
Tailoring CT Dose to Patient Size: Implementation of the Updated 2017 ACR Size-specific Diagnostic Reference Levels.Acad Radiol. 2018 Dec;25(12):1624-1631. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2018.03.005. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Acad Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29580788
-
Size-specific Dose Estimates for Chest, Abdominal, and Pelvic CT: Effect of Intrapatient Variability in Water-equivalent Diameter.Radiology. 2015 Jul;276(1):184-90. doi: 10.1148/radiol.15142160. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Radiology. 2015. PMID: 25734556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shrimpton PC, Wall BF, Hillier MC (1989) Suggested guideline doses for medical x-ray examinations. United Kingdom: Inst Phys
-
- ICRP (1996) Radiological protection and safety in medicine. In: ICRP publication 73: international radiological protection commission - PubMed
-
- ICRP (2017) Diagnostic reference levels in medical imaging. In: ICRP publication 135 international radiation protection commission
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

