Dynamic antagonism between key repressive pathways maintains the placental epigenome
- PMID: 37024684
- PMCID: PMC10104784
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-023-01114-y
Dynamic antagonism between key repressive pathways maintains the placental epigenome
Abstract
DNA and Histone 3 Lysine 27 methylation typically function as repressive modifications and operate within distinct genomic compartments. In mammals, the majority of the genome is kept in a DNA methylated state, whereas the Polycomb repressive complexes regulate the unmethylated CpG-rich promoters of developmental genes. In contrast to this general framework, the extra-embryonic lineages display non-canonical, globally intermediate DNA methylation levels, including disruption of local Polycomb domains. Here, to better understand this unusual landscape's molecular properties, we genetically and chemically perturbed major epigenetic pathways in mouse trophoblast stem cells. We find that the extra-embryonic epigenome reflects ongoing and dynamic de novo methyltransferase recruitment, which is continuously antagonized by Polycomb to maintain intermediate, locally disordered methylation. Despite its disorganized molecular appearance, our data point to a highly controlled equilibrium between counteracting repressors within extra-embryonic cells, one that can seemingly persist indefinitely without bistable features typically seen for embryonic forms of epigenetic regulation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.M. and Z.D.S. are inventors on a patent related to hypermethylated CGI targets in cancer. Z.D.S. and A.M. are co-founders and scientific advisors of Harbinger Health. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

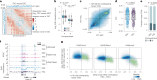




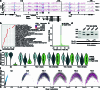
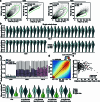
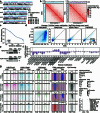
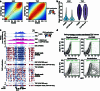


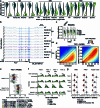

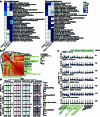
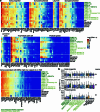
References
-
- Bird, A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature321, 209–213 (1986). - PubMed
-
- Smith, Z. D. & Meissner, A. DNA methylation: roles in mammalian development. Nat. Rev. Genet14, 204–220 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Mattei, A. L., Bailly, N. & Meissner, A. DNA methylation: a historical perspective. Trends Genet38, 676–707 (2022). - PubMed
-
- de Napoles, M. et al. Polycomb group proteins Ring1A/B link ubiquitylation of histone H2A to heritable gene silencing and X inactivation. Dev. Cell7, 663–676 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Wang, H. et al. Role of histone H2A ubiquitination in Polycomb silencing. Nature431, 873–878 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

