Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on aortic valve replacement procedures in Germany
- PMID: 37024779
- PMCID: PMC10079149
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-023-03213-y
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on aortic valve replacement procedures in Germany
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 has caused the deferral of millions of elective procedures, likely resulting in a backlog of cases. We estimate the number of postponed surgical aortic valve replacement (sAVR) and transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) procedures during the first two waves of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany.
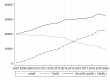
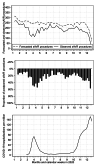
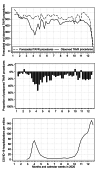
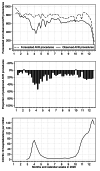
Methods: Using German national records, all isolated TAVR and sAVR procedures between 2007 and 2020 were identified. Using weekly TAVR and sAVR procedures between 2017 and 2019, we created a forecast for 2020 and compared it with the observed number of procedures in 2020.
Results: In Germany, a total of 225,398 isolated sAVR and 159,638 isolated TAVR procedures were conducted between 2007 and 2020 that were included in our analysis. The reduction in all AVR procedures (sAVR and TAVR) for the entire year 2020 was 19.07% (95%CI: 15.19-22.95%). During the first wave of the pandemic (week 12-21), the mean weekly reduction was 32.06% (23.44-40.68%) and during the second wave of the pandemic (week 41-52), the mean weekly reduction was 25.58% (14.19-36.97%). The number of sAVR procedures decreased more than the number of TAVR procedures (24.63% vs. 16.42% for the entire year 2020).
Conclusion: The first year of the COVID-19 pandemic saw a substantial postponing of AVR procedures in Germany. Postponing was higher for sAVR than for TAVR procedures and less pronounced during the second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: Covid-19; TAVI; sAVR.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DW received fees from Abiomebd, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Berlin-Chemie, Edwards Lifescience, Medtronic, and Novartis. ALL other authors have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute kidney injury after aortic valve replacement in a nationally representative cohort in the USA.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019 Feb 1;34(2):295-300. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy097. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019. PMID: 29684164
-
Length of Stay and Discharge Disposition After Transcatheter Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in the United States.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018 Sep;11(9):e006929. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.118.006929. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018. PMID: 30354596
-
Increasing Wait-Time Mortality for Severe Aortic Stenosis: A Population-Level Study of the Transition in Practice From Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement to Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2020 Nov;13(11):e009297. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.120.009297. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2020. PMID: 33167700
-
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement versus surgical aortic valve replacement in low-surgical-risk patients: An updated meta-analysis.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2020 Jul;96(1):169-178. doi: 10.1002/ccd.28520. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2020. PMID: 31631514
-
Association between surgical risk and 30-day stroke after transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2021 Mar;97(4):E536-E543. doi: 10.1002/ccd.29105. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2021. PMID: 32584507
Cited by
-
Association between social vulnerability index and admission urgency for transcatheter aortic valve replacement.Am Heart J Plus. 2024 Mar;39:100370. doi: 10.1016/j.ahjo.2024.100370. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Am Heart J Plus. 2024. PMID: 38469116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kapsner LA, Kampf MO, Seuchter SA, Gruendner J, Gulden C, Mate S, Mang JM, Schüttler C, Deppenwiese N, Krause L. Reduced rate of inpatient hospital admissions in 18 german university hospitals during the COVID-19 Lockdown. Front Public Health. 2021;8:1018. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.594117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Becher PM, Schrage B, Sinning CR, Schmack B, Fluschnik N, Schwarzl M, Waldeyer C, Lindner D, Seiffert M, Neumann JT. Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for cardiopulmonary support: insights from a german Registry. Circulation. 2018;138:2298–300. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036691. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

