Adjuvant music therapy for patients with hypertension: a meta-analysis and systematic review
- PMID: 37024863
- PMCID: PMC10077636
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-023-03929-6
Adjuvant music therapy for patients with hypertension: a meta-analysis and systematic review
Abstract
Background: High blood pressure, anxiety, depression and sleep disorder is very common in patients with hypertension. We aimed to perform a meta-analysis to evaluate the effects of adjuvant music therapy for patients with hypertension, to provide insights to the clinical management of hypertension.
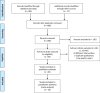
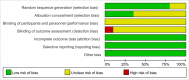
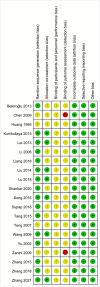
Methods: Two authors searched PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, the Cochrane Library, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, China Biomedical Literature Database, Wanfang Databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on the role of music therapy in hypertension up to Oct 15, 2022. RevMan 5.3 software was used for meta-analysis.
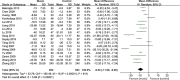
Results: A total of 20 RCTs including 2306 patients were finally included. 1154 patients received music therapy. Meta-analysis showed that music therapy can effectively reduce the systolic blood pressure(MD = - 9.00, 95%CI: - 11.99~- 6.00), diastolic blood pressure(MD = -6.53, 95%CI: -9.12~- 3.93), heart rate (MD = -3.76, 95%CI: -7.32~- 0.20), self-rating anxiety scale (SAS) score(MD =-8.55, 95%CI: -12.04~-4.12), self-rating depression scale (SDS) score(MD = -9.17, 95%CI: -13.85~-5.18), Hamilton anxiety scale (HAMA), score(MD = -3.37, 95%CI: - 5.38~- 1.36), PSQI score(MD =-1.61, 95%CI:-2.30~- 0.93) compared with routine therapy in patients with hypertension(all P < 0.05). No publication bias in the synthesized outcomes were found (all P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Music therapy can effectively control blood pressure and heart rate, reduce anxiety and depression levels, and improve sleep quality in hypertensive patients. Limited by the quantity and quality of included studies, the above conclusions need to be verified by more high-quality studies.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Care; Hypertension; Music therapy; Treatment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
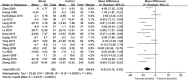

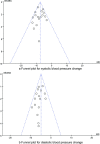
References
-
- Hypertension MCGoHRMi Multidisciplinary Expert Consensus on Heart Rate Management in Chinese Hypertensive Patients. Chin Gen Med. 2021;24(20):8–15.
-
- Xiaoting YXP, Zhe Q. Trends and influencing factors of hypertension prevalence, awareness rate, treatment rate and control rate in chinese adults from 1991 to 2015. Chin Gen Pract Med. 2022;25(7):12–6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

